Abstract
This letter considers a wireless networked control system (WNCS), where a controller sends packets carrying control information to an actuator through a wireless channel to control a physical process for industrial-control applications. In most of the existing work on WNCSs, the packet length for transmission is fixed. However, from the channel-encoding theory, if a message is encoded into a longer codeword, its reliability is improved at the expense of longer delay. Both delay and reliability have great impact on the control performance. Such a fundamental delay-reliability tradeoff has rarely been considered in WNCSs. In this letter, we propose a novel WNCS, where the controller adaptively changes the packet length for control based on the current status of the physical process. We formulate a decision-making problem and find the optimal variable-length packet-transmission policy for minimizing the long-term average cost of the WNCSs. We derive a necessary and sufficient condition on the existence of the optimal policy in terms of the transmission reliabilities with different packet lengths and the control system parameter.
I. INTRODUCTION
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) can be treated as an extension of the consumer IoT in industrial applications. One of the most important applications for IIoT is industrial control [1] with user scenarios ranging from building and process automation to more mission-critical applications, such as factory automation and power system control [2]. Wireless networked control systems (WNCSs) are composed of spatially distributed controllers, sensors and actuators communicating through wireless channels, and physical processes to be controlled. Due to the enhanced flexibility and the reduced deployment and maintenance costs, WNCS is becoming a fundamental infrastructure technology for mission-critical control applications [3]. In [4], the optimal control policy and the stability condition of a WNCS were investigated. In [5], the optimal transmission scheduling of multiple control systems over shared communication resources were studied. In [6], the uplink and downlink transmission scheduling problem of a WNCS with a half-duplex controller were considered. In [7], an event-triggered WNCS was proposed to reduce the communication cost. In [8] and [9], WNCSs with low-power and high-performance multi-hop wireless networks were investigated, respectively.
VI. CONCLUSIONS
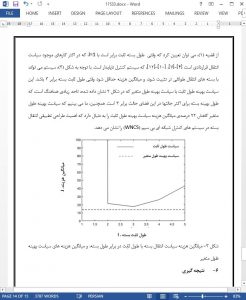
In this paper, we have proposed and optimized the variablelength packet transmission policy. We have also derived the control-system stability conditions for both the fixedlength and variable-length policies. Our numerical results have demonstrated the superior of the proposed variable-length packet transmission method in wireless control systems.