ABSTRACT
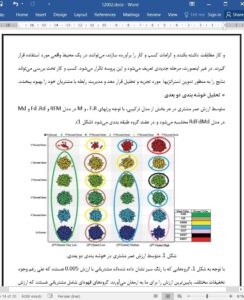
Today, increased competition between organizations has led them to seek a better understanding of customer behavior through identifying valuable customers. Customers’ expectations about the price and quality of products and services play an important role in their selection process. In online businesses, competition and price differences between suppliers is high, so discounts will attract different customers. As a result, discounts and the frequency and amount of purchases can lead to better understanding of customer behavior. Customer segmentation and analysis is essential for identifying groups of customers. Hence, this study uses a model based on RFM called RdFdMd, in which d is the level of discount used to analyze customer purchase behavior and the importance of discounts on customers’ purchasing behavior and organizational profitability. The CRISP-DM and k-mean algorithm were used for clustering. The results indicate that using the RdFdMd model achieves better customer clustering and valuation, and discounts were identified as an important criterion for customer purchases.
Introduction
Today, increased competition between markets, financial pressure, and customer bargaining power have raised issues such as increasing customer value, improving customer relationship management (CRM), and forecasting customer behavior. To increase their profitability, organizations try to maximize the value of their customers using customers’ valuable information and their differences (Chang and Tsai 2011; Farooqi and Raza 2012; Khajvand et al. 2011).
Customers have expectations about the price and quality of products and services. Price expectations play an important role in consumer choice processes (PK Kannan 2001). Pricing is an important decision for any business, and especially for emerging online retailers (Shim, Choi, and Suh 2012). Dynamic pricing is a pricing strategy where prices change over time. Economic theories argue that the dynamic pricing is inherently good for corporate profitability, because it allows companies to obtain a greater consumer surplus. Dynamic pricing is determined through up-selling, amount of discount and product packaging (Shim, Choi, and Suh 2012).