Abstract
The use of electro-osmosis for treatment of soft clay soils is a common ground improvement technique. A number of chemical, physical and mechanical interactions occur during the improvement of soil by this technique. This paper presents the results of an experimental study on the effects of treatment on the settlement and chemical and physical reactions of a clay soil. A series of experiments were conducted in a designed apparatus with electrical vertical drains (EVD) under different voltages. The experimental results showed that pH, electrical conductivity (EC) and Atterberg limits changed during the tests. In addition, electro-osmosis caused a significant increase in the settlement and undrained strength of the soil.
1. Introduction
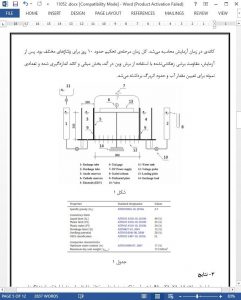
Water can have an important influence on stability of soils. The strength and stability of soil are dependent on the effective stress and hence, they are directly related to the change in pore water pressure. Dewatering is a technique of improving soil behavior by reducing pore water pressure and water content. Dewatering can be conducted by using vertical sand or gravel drains, surcharge or preloading and combination of preloading and prefabricated vertical drains (PVD) for improving the soft soil (e.g. Bergado et al., 2000; Hansbo et al., 1981; Indraratna et al., 1994; Terashi and Katagiri, 2005). When a direct current is applied to a porous medium saturated with water, the water moves towards the negative electrode (cathode) (Mohamedelhassan and Shang, 2001). This phenomenon is termed electro-osmosis. Electro-osmosis is used during dewatering to facilitate the movement of water. It accelerates the movement of water through the soil into an installed drain or well point. The water in the pores of the soil will flow out due to the ions with positive charge that are created by applying a direct current. The water content of the soil is decreased since the water can not enter in the anode (positively charged electrode) of the system. This results to the consolidation of the soil. The electro-osmosis has an advantage over other techniques as it accelerates the consolidation and strengthens the soft saturated clayey soil.
5. Conclusion
The effect of electro-osmosis on the chemical, physical and mechanical behavior of a clay soil was investigated through laboratory tests. An electro-osmotic apparatus was designed and fabricated with electrical vertical drains (EVD) to measure the desired parameters. The results showed that:The value of Ke decreases with treatment time and with increasing the applied voltage. The efficiency factor (β) is dependent on the applied voltage and it decreases with increasing the applied voltage. The values of pH and EC of anode and cathode reservoirs are changed during the treatment time and their variations are increased with increasing the applied voltage. Increasing the liquid and plastic limits decreases the liquid index leading to an increase in shear strength of the soil.