ABSTRACT
Ion acoustic solitary waves in superthermal plasmas are investigated in the presence of trapped electrons. The reductive perturbation technique is employed to obtain a forced Korteweg–de Vries-like Schamel equation. An analytical solution is obtained in the presence of externally applied force. The effect of the external applied periodic force is also observed. The effect of the spectral index (κ), the strength (f0), and the frequency (ω) on the amplitude and width of the solitary wave is obtained. The result may be useful in laboratory plasma as well as space environments.
I. INTRODUCTION
The existence of highly energetic superthermal particles in different plasma situations, which results in long-tailed distributions, is an essential part in different space13,29–34 and laboratory plasma34–40 inspections. A good number of different models have been suggested to relate this effect on nonlinear wave dynamics through phenomenological correction to the electron distribution function.
VI. CONCLUSIONS
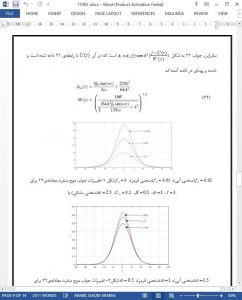
We have studied ion acoustic solitary waves in superthermal plasmas in the presence of trapped electrons. The reductive perturbation technique has been employed to derive the KdV-like Schamel equation. An analytical solitary wave solution has been derived for the Schamel equation in the presence of the externally applied periodic force. The effect of the externally applied periodic force on the ion acoustic solitary wave solution with fixed values of other physical parameters k; U0; B has been presented. The solitary wave becomes smooth when the strength (f0) of the external force decreases. On the other hand, the amplitude of the solitary wave increases when the frequency (ω) of the periodic force decreases. The result may be useful in laboratory plasmas as well as space environments.