ABSTRACT
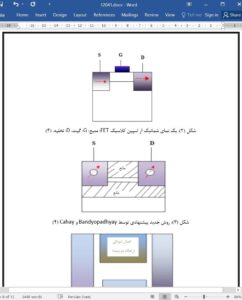
As the scaling continues to reduce the physical feature size and to increase the functional throughput, two most outstanding limitations and major challenges among others, are power dissipation and variability as identified by ITRS. This paper presents the expose, in those collective phenomena, spintronics using appropriate order parameters of magnetic moment. It shows that the benefits of the scalability to smaller sizes in the case of spintronics (nanomagnetics) include a much reduced variability problem as compared with today's electronics. In addition, another advantage of using nanomagnets is the possibility of constructing nonvolatile logics, which allow for immense power savings during system standby. However, most of devices with magnetic moment usually use current to drive the devices and consequently, power dissipation is a major issue. Spin-dependent phenomena in semiconductors may lead to devices with new enhanced functionality, such as polarized solid-state light sources (spin light-emitting diodes), novel microprocessors and sensitive biological and chemical sensors. Spintronics (or spin electronics) is an emerging field of basic and applied research in physics and engineering that aims to exploit the role played by electron spin in the solid state material. Spintronics devices make use of spin properties instead of, or in addition to electron charge to carry information, thereby offering opportunities for novel nanoelectronics devices. This paper reviews the background and current status of this subject and some applications of Spontronics.
XII. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
This paper presents a summary of Spintronics (spin based electronics), is new upcoming technology for next generation of microelectronics/nanoelectronics devices with scaling apparently approaching its fundamental limits; the semiconductor industry is facing critical challenges. In this paper authors tries to summaries, the spintronics fundamental physics, role of this technology and their applications for development for future of nanoelectronics.