Abstract
Purpose The current paper aims to evaluate the impact of investment in Intangible Assets on the corporate performance of Indian companies for a period of twelve years from 2001-2012.
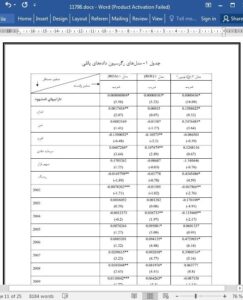
Design/Methodology Intangible assets have been measured using the ‘Intangible Assets Monitor’ method developed by Sveiby (1997). Findings The results of Panel Data Regression model reveal that Intangible Assets affect performance of companies positively after controlling for firm size, age, leverage, physical capital intensity, market share, risk, industries and year dummy.
Originality/Value Specifically considering India, the research related to the association between Intangible Assets and performance is undersized. Thus, the present study would contribute to the existing literature comprehensively.
Practical implications The study is of immense importance to the corporate managers in improving managerial insight into the significance of investment in Intangible Assets. The results direct Indian managers to understand and realize the importance of Intangible Assets and keenly invest in R&D, technology, software, advertising, CRM and human resources to further augment their performance.
1. INTRODUCTION
There is multiplicity as well as ambiguity in the identification of Intangible Assets. Grojer and Johanson (1999) and Guthrie & Petty (2000) termed these as "Soft" assets and "Weightless Wealth". Fincham and Roslender (2003) and Lev (2001) called these as “Intellectual capital” and “Knowledge assets”. Andersen (1992) describes intangible assets as non-physical in nature, capable of producing future economic net benefits. Edvinsson & Malone (1997) calls these as “hidden capabilities” of an organization. Brooking (1997) describes them as the “combination of market based intangible assets, intellectual property, human-centered and infrastructure that enables the company to function”. Strassmann (1999) defines intangible assets as the difference between the market value of a company and the book value of its tangible assets.
4. Conclusion
The present study evaluates the impact of Intangible Assets on the performance of Indian companies. The results report a positive and significant relation between Intangible Assets and performance. Resultantly the study is of immense importance to the corporate managers in improving managerial insights into the significance of investment in Intangible Assets. The results direct Indian managers to understand and realize the importance of Intangible Assets and keenly invest in R&D, technology, software, advertising, CRM and human resources to further augment their performance. Gone are the days when investment in fixed assets carried supreme importance. Rather the unobserved and unscathed assets bear equal relevance and significance. Also such investment would be more fruitful to large sized companies, older in age and with high physical capital intensity. Investment in Intangible Assets should be a part of strategic intent of managers. In order to be distinct and inimitable they should encourage investment in Intangible Assets. Such investment would definitely strengthen their internal resources and capabilities and become a source of sustained competitive advantage.