Abstract
Cloud computing has emerged as a technology that grease tasks by the dynamic allocation of virtual machines. Users pay for resources based on their demand. A cloud provider has to face many challenges. One out of the essential problem is load balancing, which suffers from many issues like premature convergence, reduced convergence speed, at first chosen random solutions, and stuck in native optima. The proposed method considered the MakeSpan parameters to handle the problem related to existing met heuristic techniques. The proposed method focuses on the mutation-based Particle Swarm algorithm to balance load among the data centers. Here an efficient load balancing algorithm is developed to minimize performance parameters like MakeSpan time and improve the fitness function in cloud computing.
I. INTRODUCTION
Cloud computing has risen as jargon in the area of highperformance computing and distributed environment. It provides users with on-demand services to a shared pool of resources over the Internet which is dynamically scalable. Cloud computing is being the most magnifying field in web technologies. It dynamically allocates the task on the virtual machine which is easily accessible to the user. One of the main challenges in cloud computing is load balancing. Load balancing is a term defined for sharing the load among the multiprocessors. The workload can be classified into various categories like CPU load, network load, memory capacity issue, etc.
IV. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
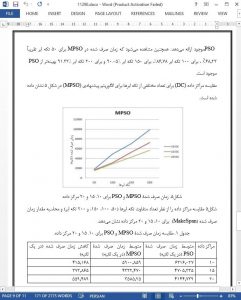
Load Balancing has always been the most significant challenge in the Cloud Computing environment. The primary objective of the proposed algorithm is to minimize MakeSpan and improve fitness function. Here proposed method uses a mutation-based particle swarm optimization. It is a natureinspired optimization technique, so the proposed method combined it with a genetic operator i.e. Mutation. Applying mutation on the best solution given by the existing PSO algorithm gave us a better MakeSpan and improved the fitness function. MPSO algorithm gives better results as compared to PSO. Here proposed method is also compared on the MakeSpan parameter. The proposed method used pre-emptive virtual machine scheduling for performing load balancing. In the future, various other metrics like throughput, average time, resource utilization, waiting time, etc. can be considered.