Abstract
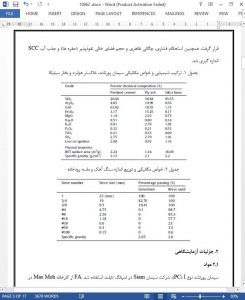
The influence of high-calcium fly ash and silica fume as a binary and ternary blended cement on compressive strength and chloride resistance of self-compacting concrete (SCC) were investigated in this study. High-calcium fly ash (40–70%) and silica fume (0–10%) were used to replace part of cement at 50, 60 and 70 wt.%. Compressive strength, density, volume of permeable pore space (voids) and water absorption of SCC were investigated. The total charge passed in coulombs was assessed in order to determine chloride resistance of SCC. The results show that binary blended cement with high level fly ash generally reduced the compressive strength of SCC at all test ages (3, 7, 28 and 90 days). However, ternary blended cement with fly ash and silica fume gained higher compressive strength after 7 days when compared to binary blended fly ash cement at the same replacement level. The compressive strength more than 60 MPa (high strength concrete) can be obtained when using high-calcium fly ash and silica fume as ternary blended cement. Fly ash decreased the charge passed of SCC and tends to decrease with increasing fly ash content, although the volume of permeable pore space (voids) and water absorption of SCC were increased. In addition when compared to binary blended cement at the same replacement level, the charge passed of SCC that containing ternary blended cement was lower than binary blended cement with fly ash only. This indicated that fly ash and silica fume can improve chloride resistance of SCC at high volume content of Portland cement replacement.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, high-volume fly ash (HVFA) concrete, with 50% or more of cement replaced by fly ash (FA) has been studied extensively. HVFA is often used to achieve good slump flow of self-compacting concrete (SCC). SCC is a new category of high-performance concrete characterized by its ability to spread into place under its own weight without the need of vibration, and self-compact without any segregation [1,2]. The use of FA in SCC reduces the dosage of superplasticizer needed to obtain similar slump flow as for concrete made with Portland cement [3]. Also, the use of FA improves rheological properties and reduces cracking of concrete due to lower heat of hydration [4,5]. However, the strengths of HVFA concrete are lower than that of pure Portland cement concrete, especially at early age due to the dilution effect and very low pozzolanic reaction [6–10].
4. Conclusions
In this study, the influence of high calcium fly ash and SF as a binary and ternary blended cement at high volume replacement on properties of SCC was investigated. From these results it can be concluded that the apparent densities of all SCC in general were notsignificantly different when containing FA and SF. The volume of permeable pore space (voids) and water absorption of SCC containing FA was higher than Portland cement control and tends to increase with increasing FA content. The influence of SF seems to decrease voids and water absorption of SCC in both binary and ternary blended Portland cement.