Abstract
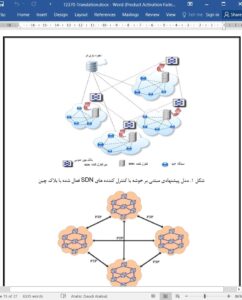
Internet of things (IoT) is one of the most emerging technologies nowadays and it is one of the key enablers of industrial cyber physical system (CPSs). It has started to participate in almost every aspect of our social life, ranging from financial transactions to the healthcare system, communication to national security, battlefield to smart homes, and so on. However, the wide deployment of IoT suffers certain issues as well, such as interoperability, compatibility, heterogeneity, large amount of data, processing of heterogeneous data etc. Among others, energy efficiency and security are the utmost prominent issues. Scarce computing resources of IoT devices put hindrances on information sharing across edge or IoT network. Indeed, unintentional or malicious interference with IoT data may lead to severe concerns. In this study, the researcher exploits the potential benefits of a blockchain system and integrates it with software-defined networking (SDN) while justifying energy and security issues. More in detail, the researcher proposed a new routing protocol with the cluster structure for IoT networks using blockchain-based architecture for SDN controller. The proposed architecture obviates proof-of-work (PoW) with private and public blockchains for Peer-to-Peer (P2P) communication between SDN controllers and IoT devices. In addition to this, distributed trust-based authentication mechanism makes blockchain even more adoptive for IoT devices with limited resources. The experimental results show that the proposed cluster structure based routing protocol outperforms the state-of-the-art Ad-hoc On-demand Distance Vector (AODV), Destination-Sequenced Distance Vector (DSDV), Secure Mobile Sensor Network (SMSN), Energy efficient secured cluster based distributed fault diagnosis (EESCFD), and Ad-hoc On-demand Multipath Distance Vector (AOMDV), in terms of energy consumption, network throughput, and packet latency. Proposed protocol help overcome the issues especially, energy management and security of the next generation industrial cyber physical systems.
1. Introduction
Industrial automation leads to the concept of smart factory on the basis of artificial intelligence (AI) and internet of things (IoT). Adaptive supply chain management, human–robot integration, production quality and predictive maintenance are a few examples of the industrial automation and cyber physical systems (CPSs). A huge number of sensors are deployed in the field for effective and efficient industrial automation and such a vast deployment lead to the issues of interoperability, heterogeneity among devices, processing and dealing of big data, storage of data, energy management, safety and security.
5. Conclusion and future work
Next generation industrial cyber physical systems (CPSs) require artificial intelligence (AI) empowered solutions to overcome the issues of heterogeneity of devices, big data generation by the sensors, data streaming, processing of heterogeneous unstructured data and the data security. The increasing trend of smart and intelligent services triggers the avalanche in the IoT network and their related services. To provide secure and efficient services, there is an urgent need to manage the computing and energy scarcity problem of IoT. This study focuses on mitigating some of the challenges related to IoT’s network. By exploiting the power of AI, we have proposed architecture for IoT networks to enhance security and improve energy efficiency. We integrated the two emerging AI based technologies namely, blockchain and SDN, and leverage their potential benefits in terms of efficient data analysis, data security and efficient energy management. For the IoT network with blockchain support for the SDN controller, a cluster-based framework was introduced. On both public and private networks, the blockchain is used. The resource-hungry component of PoW is eliminated to tailor the blockchain for IoT capabilities. This method saves a large amount of energy, boosts data transfer rates, and reduces latency. Extensive testing has shown that the proposed model outperforms both the basic blockchain approach and current routing protocols. This study will In the IoT domain, we hope to develop a high-level P4 architecture with blockchain support in the future.