Abstract
Power grids are being enhanced by integrating the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) to make them more reliable, economic, efficient, and environmentally friendly. The integration of power grids with ICT to build Smart Grids (SGs) has reduced costs and improved their performances. But, on the other hand, this has also brought the cyber security threats as well. In traditional ICT systems, the end devices are the powerful systems which have high computation power and memory capacity to perform the intense computations to avoid cyber security threats, whereas most of the end devices in SG lack these capabilities. Incorporating the security in the early stages of SG development through systems security requirements engineering can reduce the potential cyber security threats. This paper presents the results of applying Security Requirements Engineering Process (SREP) on the SG wireless network, and proposes the potential solutions that can be implemented such as using Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM)-enabled Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) with Global Positioning System (GPS) support.
I. INTRODUCTION
The success of any system relies on effectively capturing the stakeholders’ needs in requirements specification [1], [2], [3]. Some studies show that the cost of adding the requirements in later stages of the system development could be 10 to 200 times higher [4], [5]. Jones et al. [6] propose that, in most of the system development projects, fixing the requirements, design and code defects cost 40% to 50% of the total system development efforts. In addition, more than 50% of the defects originate during the systems requirements engineering; if not done properly it can seriously impact the system. Flaws in requirements typically cost 25% to 40% of the total project costs [7]. This highlights the importance of the requirements specifications as the vital step in the systems development lifecycle. Similarly, security requirements also have greater impact on the fault-free functioning of any system.
V. CONCLUSION
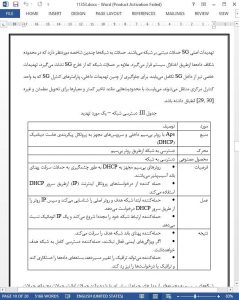
This paper presents the step-by-step systematic application of the systems security requirements engineering method to elicit, categorize and prioritize security requirements for SG wireless networks. We elicited, categorized, and prioritized 43 security requirements. We found 21 of them to be of high priority, 16 of medium priority and 6 of low priority. We found 7 data-related vulnerabilities in house-to-grid communication and 10 network-related vulnerabilities in intra-grid communications. We found a total of 13 threats. We identified 3 types of threats to be more harmful to SG when active.