Abstract
Surface ruptures caused by strong earthquakes are one of the most concerning issues for construction projects. In this paper, geotechnical centrifuge model tests is performed to successfully simulate the reverse faulting process. Using a linear laser displacement sensor (LLDS) and the particle image velocimetry (PIV) technique, the surface deformation process and faulting behaviours are studied in dry and wet sand with a thickness of 40 m above a bedrock surface. Based on an analysis of high-precision surface monitoring data, the soil rupture process is divided into four stages: the overall uplift period, inclination deformation period, scarp growth period, and deformation slowdown and lag period. In addition, the characteristics of the soil deformation and the propagation behaviour of the upper fault tip are obtained. This experiment and related achievements can provide references for further understanding the deformation of thick soil layers caused by reverse faulting.
1. Introduction
The neotectonic activity in China is strong, and strong earthquakes can rupture the surface; moreover, as active faults are widely distributed, various long-distance linear engineering projects are being constructed across faults [1]. Movement along a fault associated with a strong earthquake can rupture and deform the surface, causing great damage to structures (such as buildings on the surface), underground pipelines and tunnels and seriously threatening people’s lives and property [2]. As examples, the magnitude 7.6 Chi-Chi earthquake in 1999 and the magnitude 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake in 2008 caused large-scale surface ruptures, and numerous dam foundations, road bridges and underground pipelines were damaged [3].
6. Conclusion
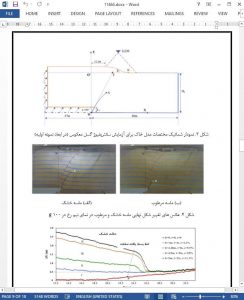
In this paper, the deformation of soil within 40 m of a reverse fault is simulated by a centrifuge model test at 100g, and the deformation characteristics of dry and wet sand resulting from a bedrock fault with a dip angle of 60 are obtained. The results can provide references for further understanding the failure mechanism of soil overlying a concealed reverse fault. The following main research conclusions are drawn.
(1) At the beginning, the surface is in an overall uplift stage, and a scarcely obvious scarp is observed. At this moment, the soil comprises three distinct zones: the hanging wall uplift zone, foot wall quiescent zone and intermediate shear zone. The surface begins to deform when the amount of imposed offset accounts for approximately 2.2% of the thickness of the soil.