Abstract
A new adaptive protection method for distribution network is proposed, which is suitable for distributed generation (DG) access. According to the operation mode of the system and the topology of the network, this method performs an equivalent transformation on the protection backside network and eliminates the influence of DG on each branch current according to the branch contribution factor matrix. On this basis, adaptive main protection and backup protection are constructed. Compared to the traditional current protection, this method increases the protection range of the main protection and the backup protection, and the calculation is simple and easy to be set. The simulation results show that this method is not affected by DG access, and can satisfy the adaptive functions of protection in the case of symmetric or asymmetric faults.
1 Introduction
With the increasing problems of energy and environment, distributed generation (DG) is increasingly becoming a hot topic for its high efficiency, compatible environment and adaptability to renewable energy. The combined operation of DG and large grid have the characteristics of power supply flexibility, reliability and security [1] and other social benefits, which also with the peak load shifting, reduce network losses and improve the utilisation of existing equipment [2] and other economic benefits. However, the access of DG changed the single-source radiating structure [3] of the distribution network, the running status of the power system and the level of fault, which posed a new challenge to relay protection [4–6].
5 Conclusion
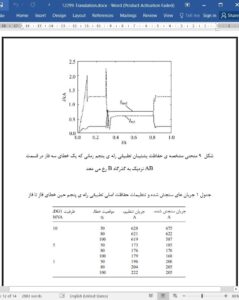
On the basis of the influence from DG on the relationship between traditional protection setting and cooperation, a new adaptive protection method for distribution network is proposed in this paper. Simulation results show that this method has the following characteristics:
(i) Not affected by the DG access, and therefore solving the problem of distribution network protection with DG distribution feeder.
(ii) The protection range of the main protection can still reach 80% of the line, and the protection range of the backup protection can extend to more than 40% of the subordinate line under the adverse situation of two-phase short circuit. Compared to the traditional current protection, this method significantly increases the protection scope of the main protection and backup protection.
(iii) Not affected by the type of fault and satisfied with reliability of protection under both symmetrical and asymmetrical faults.