Abstract
Recent advances allow us to propose antibodies targeting beta-2-glycoprotein I (β2-GPI) as the most specific antibodies associated with anti-phospholipid syndrome (APS). Therefore, there is now a crucial need for powerful biological assays to adequately monitor them. It is well established that these antibodies recognize mainly cryptic epitopes, which requires a great deal of consideration in the choice of laboratory tests to identify these antibodies. To this end, an update on the pathophysiological role of β2-GPI and a meta-analysis were conducted providing an overview of the current progress towards anti-β2-GPI detection.
1. History and STATE of the art
1.1. From syphilis diagnosis to the anti-cardiolipin autoantibodies
While the definition of the antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) was established in 1999 [1], the biological history of the antiphospholipid antibodies (APLA) started long before that in the first decade of the 20th century with development of assays for the diagnosis of syphilis. Indeed, Wassermann was the first in 1906 to apply the complement fixation reaction, previously described by Bordet and Gengou, in a new test for the diagnosis of syphilis using fetal liver extracts from dead embryos with congenital syphilis as an antigenic source [2]. This antigenic source was shortly replaced with an alcoholic extract from nonsyphilis beef heart by Landsteiner who had then developed the Venereal Disease Research Laboratory Test (VDRL). Later on in 1941, Pangborn characterized mitochondrial phospholipids, called cardiolipin because of its cardiac origin, as the main antigenic source from the beef extract [3]. This improvement led to the development of more accurate syphilis tests using purified cardiolipin [4]. It was then shown that cardiolipin was in fact phosphatidylglycerol, though we kept the cardiolipin appellation.
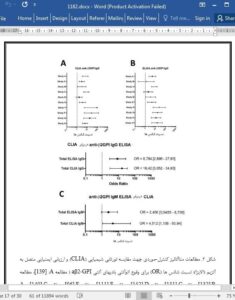
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, several advancements were made in the biological diagnosis of APS over the last thirty years and the discovery of the central role played by aβ2-GPI in APS. This has led to the inclusion of aβ2-GPI G/M autoantibodies in the APS diagnostic criteria of 2006 with high hopes, but those hopes have been incompletely satisfied while some improvements were made since that time.