Generally, land fragmentation is a universal trait of all agricultural systems which affects farmland productivity and no one had documented a rural society where there was no land fragmentation. Hence, this study sought to ascertain the effects of land fragmentation on farmland productivity in the highland districts of Northwestern Ethiopia by using cross-sectional data collected from 240 respondents during 2015/16 production seasons and analyzed by using linear and Cobb-Douglass production functions. In land productivity model, 38% of variations in farmland productivity are explained by variations in independent variables including land fragmentation parameters. Average farmland size of 1.25 ha was obtained as minimum size that can generate minimum food and cash requirement of an average family of five adult equivalents. Hence, the government should come up with land use policy and population growth controlling program, which enables determining minimum economic farmland size, improving land productivity, and finding ways to strengthen off-farm activities and livestock sector to absorb more labor and enhance means of generating more income so as to decrease minimum farmland size required.
1. Introduction
Agriculture has always been an important sector in Ethiopia which is serving 85% of the population either directly or indirectly that placed the smallholder farmers as central focus of development policies and strategies. However, it had been characterized by a very low growth rate, estimated at about 1.4% per annum in real term, which was less than the growth rate of population, that is, 2.49% per annum, during the last three decades [1].
The rational use of agricultural land is influenced by land use limitations. One of the obstacles for agricultural development is land fragmentation [2–4]. Land fragmentation is defined as the situation in which a single farm or ownership consists of numerous spatially separated plots [5]. Likewise, according to Bizimana et al. [6] land fragmentation refers to farmers operating two or more geographically separated tracts of land, taking account of the distances between those parcels. Dominant problem associated with land fragmentation is the small size, irregular shape, and dispersion of parcels [7, 8]. With this statement, in Ethiopia, about 92.26% of rural households operate on holdings of mean 1.4 ha which constitutes 72% of total crop area. The number of households operating on holdings smaller than or equal to 1 ha (mean 0.73 ha) constitutes 72.1% of the total while the national average holdings estimate is about 0.8 ha [9]. This indicates that agricultural land fragmentation is a widespread phenomenon in highland areas of the country. The major causes are being land distribution and redistribution, inheritance rules, and risky peasant agriculture. In line with this Rahameto [10] stated that land fragmentation was widespread in North as well as South under all tenure systems and in many parts of Ethiopia
5. Conclusion and Policy Options
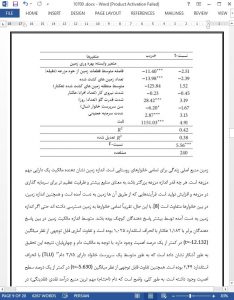
(i) The result showed that there is a significance mean differences on productive resources ownership among smallholder farmers.
(a) Therefore, intervention strategies focused on improving accessibility of resources, that is, through provision of communal land, are crucial to minimizing income disparities between smallholder farmers who lease out their land and who plough by themselves.
(b) Moreover, improving the productivity of livestock sector could have an immense impact to improve the household income so that food security status at household level would be above threshold level.