Abstract
Purpose The aim of this study was to assess the emotional intelligence of nurses caring for COVID-19 patients.
Methods This was a descriptive cross-sectional study that was conducted from May to July 2020 in Tehran, Iran. Nurses caring for patients with COVID-19 were requested to fill in Bradbury and Graves's questionnaire online using a questionnaire in electronic format.
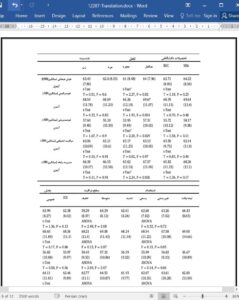
Results Finally 211 nurses completed the questionnaires. Most of the nurses were working in critical care wards and caring for critical patients (61.6). Nurses' emotional intelligence was reported to be 63.19 (8.22). In general, the nurses' emotional intelligence was moderate. Between the dimensions, self-awareness and self-management had the highest scores. Also, the lowest score was related to self-management. The ward type and complexity of care had no effect on the scores of emotional intelligence. Nurses caring for patients with moderate disease severity had a higher relationship management score than nurses caring for critically ill patients (P < 0.05).
Conclusion The total score of emotional intelligence was moderate. Due to the continuation of the COVID-19 pandemic and the possibility of mental and physical fatigue of health care workers, improving emotional intelligence can be effective in resilience and stability of the psychological status of employees.
Conclusion The EI of nurses caring for patients with COVID19 was moderate. In terms of dimensions, the highest score was related to individual abilities (self-awareness and self-management). According to the results of the present study, the development of emotional intelligence based on the characteristics of nurses is very important in recognizing and managing their emotions. Due to the continuation of this pandemic and the possibility of mental and physical fatigue of health care workers, improving emotional intelligence can be effective in resilience and stability of the psychological status of employees.