Abstract
Two key traits of 5G cellular networks are much higher base station (BS) densities-especially in the case of low-power BSs-and the use of massive MIMO at these BSs. This paper explores how massive MIMO can be used to jointly maximize the offloading gains and minimize the interference challenges arising from adding small cells. We consider two interference management approaches: joint transmission (JT) with local precoding, where users are served simultaneously by multiple BSs without requiring channel state information exchanges among cooperating BSs, and resource blanking, where some macro BS resources are left blank to reduce the interference in the small cell downlink. A key advantage offered by massive MIMO is channel hardening, which enables to predict instantaneous rates a priori. This allows us to develop a unified framework, where resource allocation is cast as a network utility maximization (NUM) problem, and to demonstrate large gains in cell-edge rates based on the NUM solution. We propose an efficient dual subgradient based algorithm, which converges towards the NUM solution. A scheduling scheme is also proposed to approach the NUM solution. Simulations illustrate more than 2x rate gain for 10th percentile users vs. an optimal association without interference management.
I. INTRODUCTION
SMART densification & heterogeneity in base station (BS) deployments and massive MIMO are considered as two of the most important technologies in 5G cellular systems [1]–[3].1 The massive MIMO regime is the setting when the number of antennas at a BS is significantly larger than the number of users that are simultaneously served by the BS [4]–[6]. In this paper, various aspects such as user association, load balancing, scheduling and interference management are considered for future networks with massive MIMO deployments where these technologies are adapted together.
VIII. CONCLUSION
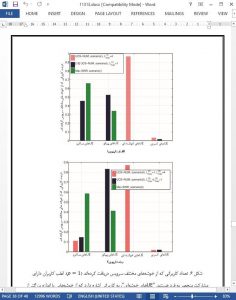
In this paper, we investigate the joint optimization problem of user association and interference management in the massive MIMO HetNets. We consider both LJT and RB blanking approaches for interference management. We first provide the instantaneous rate from BS clusters by exploiting massive MIMO properties, namely the rate hardening and the independence of peak rate from the user scheduling. We then formulate a convex NUM problem to obtain the optimal user-specific BS clusters and the corresponding resource allocation. The unified formulation can be applied to both LJT and blanking approaches, as well as the case where macro and small BSs use orthogonal resources. We further propose an efficient dual subgradient based algorithm, which is shown to converge towards the NUM solution.