Abstract
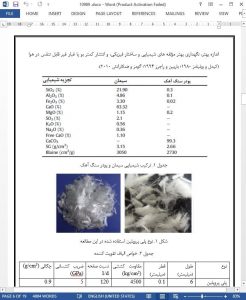
Increasing quantity of scrap tires are potential sources of fire and health hazards. Rubberized pavement is being considered as one of the promising and sustainable solutions to this current environmental and economic crisis in the world. This research focused on finding the best way of producing paving concrete with the use of tire rubber waste as a component material. Therefore, Tire Rubber Crumb (TRC) was used as a partial sand replacement (5%, 10% and 15%) material in the mix design of self-compacting concrete. Self-compacting concrete (SCC) is considered an energy efficient material; because it reduces on-site working and does not need any compacting energy. Fine aggregates with fineness modulus of 2.9, specific gravity of 2.64 (g/cm3) and water absorption of 1.5% and coarse aggregates with maximum size of 12.7 mm, specific gravity of 2.68 (g/cm3) and water absorption of 0.8 were used in this research. According to the results of this study, fresh concrete tests showed that both fiber and TRC have negative effects on rheological properties of fresh concrete. Furthermore, the hardened concrete tests showed that TRC decreases compressive strength, tensile strength, flexural strength, abrasive strength and modulus of elasticity while increasing water absorption of SCC. Therefore, polypropylene fibers were added into SCC specimens containing TRC and resulted in significant increases in compressive, tensile, flexural and abrasion strength but had no considerable effect on the modulus of elasticity of these specimens. Moreover, the presence of fiber in rubberized SCC decreased water absorption based on evaluation of ultrasonic waves velocity.
1. Introduction
Rapid growing amounts of rubber tire wastes is a serious consequence of significant increase in the number of vehicles. The high volume storage of scrap tires has deleterious effects on the environment. Waste tires would lead to significant health and environmental concerns if not recycled or discarded properly. One of the recent way of tackling this challenge is to apply this type of wastes into civil engineering infrastructures. Shredded rubber tires have been used as aggregates in concrete and gained popularity over the last years. Many studies have been conducted on using Tire Rubber Crumb (TRC) in different types of concrete in order to study crumb rubber effects on these concrete mechanical behavior (Meddah et al., 2014; Murugan & Natarajan, 2015; Elchalakani, 2015).
5. Conclusion
Rubberized pavement is being taken into account as a sustainable approach to deal with the environmental and economic crisis of large amount of waste tire in the world. In addition, since selfcompacting concrete (SCC) reduces the amount of energy needed for filed working, it is considered as an energy efficient material which is sustainably suitable for pavement construction. In the present study, physical properties of SCC containing TRC as partial sand replacement and also the effect of addition of polypropylene fiber to this type of concrete have been investigated and the following results have been obtained.
1. The results of tests carried out on fresh concrete signifies the negative effects of increasing fiber content and TRC in concrete on rheological properties of fresh SCC.