Abstract
Day by day demand of Electricity is increasing so, in order to fulfill this demand we need to increase generation of power. Because of this increasing demand, non-renewable energy sources are on the verge of extinction so the solution is to use renewable energy sources. One such solution is to connect DG having renewable energy sources in power system. But the insertion of DG has some impact on a power system.
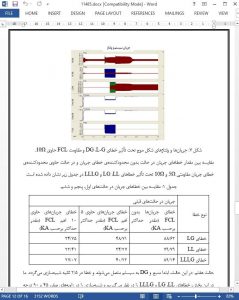
This paper deals with the evaluation of the impact of DG on the protection of power system. The work presented in this paper consists of a simulation of a radial power system in PSCAD /EMTDC software. Monitoring of both fault current and the load current is done in the simulation. The impact of DG on fault current under the influence of LG, LL and LLLG fault with and without protection is studied Maximum magnitude of fault current is found in case of LLLG fault. Also, the impact of resistive fault current limiter on the magnitude of fault current is studied. Both DG and source is protected from fault current by using overcorrect protection with pick up value of 2kA and 4kA respectively.
I. Introduction
The performance of distribution system is affected by distributed generation in various ways. As DG is related to renewable energy for lowering the environmental impact of power generation indicate a large scope for DG in future. DG improves voltage Profile but interfere with voltage regulation [1],[2]. The losses in a circuit can be minimized if DG is connected near to the load. The existing system did not deal with generation at distribution substation on radial feeder so such system where not designed to handle such power would be sent back to the source. Hence, accountable effect on the operation of existing protection may occur both false tripping and non-operations of protective devices are possible [3].
VIII. CONCLUSION
The presence of Distributed Generation may cause higher fault currents that are over the breaking capacity of circuit breakers. Therefore, existing protection devices are exposed to more electrical stress than normal.
The cases presented in this paper shows that by adding DG the current drawn by the induction motor is contributed by both source and DG. Also, the DG contributes to the fault so it is found that magnitude of fault current increases with the insertion of DG. By providing instantaneous overcurrent protection both source and DG are protected.