Abstract
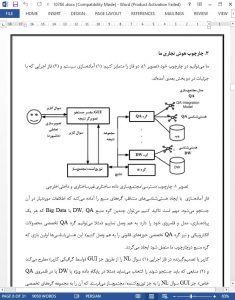
Business Intelligence (BI) applications allow their users to query, understand, and analyze existing data within their organizations in order to acquire useful knowledge, thus making better strategic decisions. The core of BI applications is a Data Warehouse (DW), which integrates several heterogeneous structured data sources in a common repository of data. However, there is a common agreement in that the next generation of BI applications should consider data not only from their internal data sources, but also data from different external sources (e.g. Big Data, blogs, social networks, etc.), where relevant update information from competitors may provide crucial information in order to take the right decisions. This external data is usually obtained through traditional Web search engines, with a significant effort from users in analyzing the returned information and in incorporating this information into the BI application. In this paper, we propose to integrate the DW internal structured data, with the external unstructured data obtained with Question Answering (QA) techniques. The integration is achieved seamlessly through the presentation of the data returned by the DW and the QA systems into dashboards that allow the user to handle both types of data. Moreover, the QA results are stored in a persistent way through a new DW repository in order to facilitate comparison of the obtained results with different questions or even the same question with different dates.
1 Introduction and motivation
Nowadays, the available information, mainly through the Web, is progressively increasing. According to the 2011 Gartner Group report (Gartner Group report 2011), worldwide information volume is growing annually at a minimum rate of 59% annually. Thus, the information that could be potentially used by a company is progressively increasing. This information is accessible from any computer, and an important percentage of this information is unstructured and textual, such as the one generated by Social Networks (e.g. Twitter or Facebook). The structured data is predetermined, well defined, and usually managed by traditional Business Intelligence (BI) applications, based on a Data Warehouse (DW), which is a repository of historical data gathered from the heterogeneous operational databases of an organization (Inmon 2005; Kimball and Ross 2002). The main benefit of a DW system is that it provides a common data model for all the company data of interest regardless of their source, in order to facilitate the report and analysis of the internal data of an organization. However, there is a wide consensus in that the internal data of organizations to take right decisions is not enough, even more in current highly dynamic and changing markets where information from competitors and clients/users is extremely relevant for these decisions. Thus, the main disadvantage of traditional DW architectures is that they cannot deal with unstructured data (Rieger et al. 2000).
6 Conclusions and future research
In this paper, we have proposed a full framework with the aim to integrate the internal structured data of an enterprise, with external unstructured data. This framework has been tested on an Electronic Product Sales scenario, in which the enterprise’s marketing department wants to analyze sales to identify possible features useful for making new promotions by accessing and acquiring external data from the Web competitors. In this case scenario, the advantages of our proposal have been shown. Specifically, a set of 97,799 Web pages of electronic products have been crawled and accessed by a Question Answering (QA) system on a specific question. This question has been also posed to a DW system with the internal information of the enterprise, and the information returned by both the QA and the DW systems has been presented to the user through a dashboard that helps the decision makers to compare instantaneously internal figures with figures from competitors, thereby allowing taking quick strategic decisions based on richer data. Moreover, the QA results are stored in a persistent way through a new DW repository in order to facilitate comparison of the obtained results with different questions or even the same question with different dates.