Abstract
Interest in the field of performance assessment of health care structures has grown in recent decades. In fact, the possibility of determining overall performances of health care structures plays a key role in the optimization of resource allocation and investment planning, as it contributes to reducing the uncertainty of future performance. In this context, key performance indicator (KPI) tools have been developed to assess the performance of health care structures from process, organizational, cost, financial, and output points of view. In practice, they are periodically calculated, and the effect of several KPIs on the overall performance of health care structures is determined by management through human judgment or software that provides synthetic dashboards. Given their non-stationary nature, performance assessment and forecasting are generally tackled by employing adaptive models, but these approaches cannot reflect the holistic nature of performance itself, nor take into account the impact of KPIs on the overall performances. In order to overcome these shortcomings, this study presents an expert system whose engine relies on fuzzy sets, in which the input–output relations and correlations have been modeled through inference rules based on time-series trends. The focus is on the financial performance assessment of a health care structure, such as a hospital. The approach is of an interdisciplinary kind, as several indicators were taken as inputs that relate to output, process, and cost KPIs, and their impact on the output measure, which is of a financial kind (namely the total reimbursement). The output measure calculated by the expert system was then compared with that predicted using only adaptive forecasting models, and the error with respect to the actual value was determined. Results showed that measures determined by fuzzy inference, able to effectively model actual input–output relations, outperform those of adaptive models.
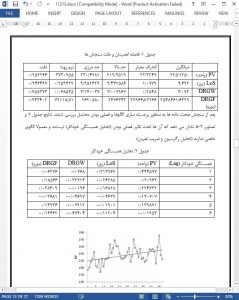
5. Conclusions
KPI-based health care performance assessment is a topic of relevant interest, as it involves considering non-stationary KPI behavior and the holistic nature of health care performances. In this study, an expert system for financial performance assessment was designed, relying on fuzzy sets as an inference engine. Unlike traditional decision-making systems, which are used to determine a KPI panel synthesized by human judgments, the fuzzy approach allows us to determine the simultaneous impact that several KPIs can have on health care performances, taking into account the correlation between input variables and the output variable. In order to test the effectiveness of the proposed methodology, a comparison between fuzzy inference engine forecasting and traditional adaptive models was made. The results showed that a comprehensive approach, such as that proposed, outperforms adaptive forecasting methods in minimizing MAD and MAPE of measures, as it takes into account the correlation between variables and their effect on the output variable. The methodology proposed can be considered sufficiently general, as new input–output variables can be added in order to better reflect the real system characteristics.