Abstract
Depression has become a major public health issue worldwide. According to the model of personality and depression, personality traits can influence the onset and/or maintenance of depression. Although some studies have explored the narcissism–depression association, their results have been inconsistent due to the multidimensional nature of narcissism, and much less is known about the mediating mechanisms underlying this relationship. A total of 831 young adults (368 males, 455 females, and 8 undisclosed) participated in this research. They filled out a set of standardized instruments, which measured variables including demographics, narcissism, depression, life satisfaction, and perceived social support. Results showed that narcissistic admiration was negatively related to depression, while narcissistic rivalry was positively correlated with depression. Perceived social support and life satisfaction were two potential mediators in the relationship between narcissism and depression. Our results demonstrated that narcissistic admiration is probably positive, while narcissistic rivalry might be negative with mental health. In future research, we need to gain a more nuanced understanding of narcissism.
1. Introduction
The World Health Organization predicted that depression will be the largest cause of human disability globally by 2030 (World Health Organization, 2012). According to the model of personality and depression, personality traits influence the onset and/or maintenance of depression (Klein, Kotov, & Bufferd, 2011). Narcissism is an important personality trait to consider due to the difficulties in maintaining mental health among maladaptive narcissists (Konrath & Bonadonna, 2014). Although some studies have explored the relationship between narcissism and depression (e.g., Brailovskaia, Bierhoff, & Margraf, 2019; Papageorgiou, Denovan, & Dagnall, 2019), their findings have not been consistent, and much less is known about how narcissism relates to depression. In fact, knowing mediating processes that explain the risk of depression is crucial because this knowledge may guide the development of interventions to prevent or reduce depression (Orth & Robins, 2013). Therefore, this study aimed to explore the narcissism-depression association, and their underlying mechanisms.
5. Conclusion
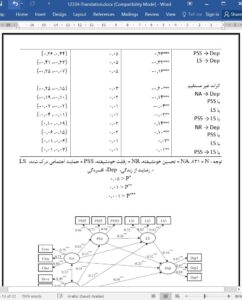
In summary, this study established an integrated mediating model to clarify the narcissism-depression associations and their underlying mechanisms. Specifically, narcissistic admiration and rivalry differently linked with depression, perceived social support and life satisfaction. The narcissism-depression relationship probably mediated by perceived social support and life satisfaction. Our results demonstrated that narcissistic admiration is probably positive, while narcissistic rivalry might be negative with mental health.