Abstract
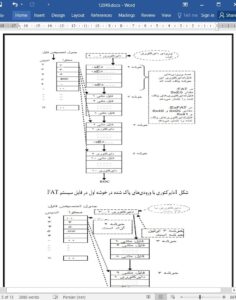
The Extend File Allocation Table (ExFAT) is the future file system for embedded storage devices. The File Allocation Table (FAT) file system de-facto file system for embedded storage devices such as Multimedia Cards (MMC) / Secure Digital (SD) / Micro SD cards, NOR, NAND flash memories. The MMC and SD card associations classify the ExFAT as the standard file system for storage flash cards of more than 32 Giga Bytes (GB) of size. This paper implements the directory compaction techniques for both FAT and ExFAT file system to improve the availability of the user space in the file systems.
1. Introduction
The FAT [1] is widely used file system in tablet personal computers, mobile phones, digital cameras and other embedded devices for data storage and multi-media applications such as video imaging, audio/video playback and recording. The initial version of FAT file system was FAT12 by Microsoft Corporation, later it was extended as FAT16 and further as FAT32 to support higher storage capacity. The FAT file system was initially developed to use on floppy disks and hard-drives. Since most of the Personal Computer (PC) s implements the FAT file system, this file system has become a default and world-wide compatible storage format for embedded devices. Usually the device with the implementation of FAT is recognized as removable storage media in a PC. The Flash memories are default choice of any embedded device as they are lowpriced, smaller size and higher storage capacity. Even though FAT file system does not define flash management techniques such as Wear-Levelling and Bad Block management, the embedded devices implements this file system along with the dedicated flash block management algorithms.