Abstract
Fault tolerance is among the most imperative issues in cloud to deliver reliable services. It is difficult to implement due to dynamic service infrastructure, complex configurations and various interdependencies existing in cloud. Extensive research efforts are consistently being made to implement the fault tolerance in cloud. Implementation of a fault tolerance policy in cloud not only needs specific knowledge of its application domain, but a comprehensive analysis of the background and various prevalent techniques also. Some recent surveys try to assimilate the various fault tolerance architectures and approaches proposed for cloud environment but seem to be limited on some accounts. This paper gives a systematic and comprehensive elucidation of different fault types, their causes and various fault tolerance approaches used in cloud. The paper presents a broad survey of various fault tolerance frameworks in the context of their basic approaches, fault applicability, and other key features. A comparative analysis of the surveyed frameworks is also included in the paper. For the first time, on the basis of an analysis of various fault tolerance frameworks cited in the present paper as well as included in the recently published prime surveys, a quantified view on their applicability is presented. It is observed that primarily the checkpoint-restart and replication oriented fault tolerance techniques are used to target the crash faults in cloud.
1. Introduction
Cloud computing has been prominently existing as an on-demand computing service paradigm and immensely benefiting the small-scale users as well as large-scale commercial and scientific applications. It is defined as a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction [1]. On-demand access, resource autonomy, rapid elasticity and always-on availability are the primary characteristics of cloud computing [2]. Cloud resources are provisioned using standard protocols (IAM, OAuth, OpenID, etc. for authentication; and AMI, OVF, SOAP, REST, etc. for data and workload migration [3]) to create the wider acceptability of cloud services. Besides this, cloud offers greater business agility at the reduced cost which further attracts a vast user base. A recent survey conducted over 433 enterprise respondents containing 1000+ employees reveals that 95% of the respondents are using cloud [4]. Kazarian et al. [5] reported 91% adoption of cloud by the IT professionals in more than 3000 small and midsize businesses. Anticipating its vast benefits, distinguished IT organizations (such as Amazon, Microsoft, IBM, Google, Yahoo, etc.) are into the foray to deliver cloud services.
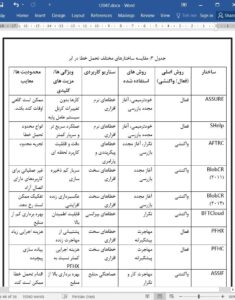
7. Conclusions
Fault tolerance has been one of the major issues in cloud computing environments. Dynamic infrastructure and complex configuration are among the key reasons. In this paper, different fault types (along with their causes) and various fault tolerance approaches in cloud computing have been discussed in a systematic manner. Eminent fault tolerance frameworks have also been surveyed in terms of their basic approach, fault applicability and key features. Following conclusions have been made:
• Researchers are more motivated towards addressing crash faults rather than byzantine faults.
• Reactive fault tolerance methods are more often applied rather than proactive ones.
• Higher overheads and complex implementations are observed as the core reasons behind the reluctance of researchers towards proactive approaches.
• Replication is the most applied fault tolerance technique followed by checkpoint restart and job migration respectively.
• In many frameworks, checkpoint restart and job migration are used as auxiliary techniques with replication.