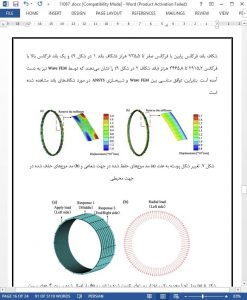
Abstract
Periodically stiffened shell structures are widely used due to their excellent specific strength, in particular for aeronautical and astronautical components. This paper presents an improved Wave Finite Element Method (FEM) that can be employed to predict the band-gap characteristics of stiffened shell structures efficiently. An aero-engine casing, which is a typical periodically stiffened shell structure, was employed to verify the validation and efficiency of the Wave FEM. Good agreement has been found between the Wave FEM and the classical FEM for different boundary conditions. One effective wave selection method based on the Wave FEM has thus been put forward to filter the radial modes of a shell structure. Furthermore, an optimisation strategy by the combination of the Wave FEM and genetic algorithm was presented for periodically stiffened shell structures. The optimal out-of-plane band gap and the mass of the whole structure can be achieved by the optimisation strategy under an aerodynamic load. Results also indicate that geometric parameters of stiffeners can be properly selected that the out-of-plane vibration attenuates significantly in the frequency band of interest. This study can provide valuable references for designing the band gaps of vibration isolation.
1. Introduction
Thin shell structures have been widely used to reduce weight for modern mechanical systems, in particular for aeronautical and astronautical components Stiffeners are usually employed to improve the mechanical behaviour of thin shell structures, via forming a higher specific-strength structure, however, a stiffened shell structure is still susceptible to vibration. It is always difficult to suppress vibration due to natural modes inherent to the structure, in particular in the high frequency range. In engineering applications, the intense resonance may occur due to vibration and lead to severe hazards to machines [1e3].
5. Conclusions
An improved Wave FEM method has been put forward by considering the boundary and the internal nodes accurately in a cylindrical coordinate and by introducing a wave selection idea. Therefore the vibration band-gap characteristics of the stiffened periodic shell can be achieved efficiently. The optimisation method GA was adopted for the design of a fan casing. The configuration parameters are optimised so that the wave does not span across the concerned broad frequency range. The vibration isolation method developed in this article can provide a reference for the practical application on the optimisation design of the stiffened shells.