Abstract
The paper presents a reliability network equivalent approach to distribution system reliability assessment. In this technique, a general feeder is defined and a simple set of equations is utilised. The basic general feeder equations and the reliability network equivalent provide a practical technique for evaluating the reliability of complex radial distribution systems. The procedure is illustrated by application to a relatively simple but practical system example.
1 Introduction
The main thrust of power-system-reliability evaluation over the past few decades has been concentrated on generation and transmission, with relatively little effort applied to the distribution domain, particularly lowvoltage distribution systems. The basic reason for this is that generation and transmission systems are capital intensive and their inadequacy can have widespread catastrophic consequences for both society and its environment. The contribution of distribution systems to overall customer unreliability is, however, quite significant. Utility statistics show that distribution-system failures account for approximately 80% of the average customer interruptions [ 11. The reliability of an individual customer load point is very dependent on the topology, design and operation of the local-distribution system.
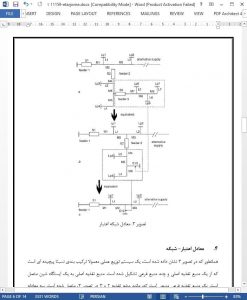
7 Conclusion
This paper illustrates a practical technique for complex-radial-distribution-system reliability evaluation. A general feeder is defined and a set of basic equations is developed based on a general-feeder concept. A complex radial-distribution system is reduced to a series of general feeders using reliability network equivalents. Basic equations are used to calculate the individual load-point indexes. The reliability-network-equivalent method provides a simplified approach to the reliability evaluation of complex distribution systems. Reliability evaluations for several practical test distribution systems have shown this technique to be superior to the conventional FMEA approach. This method avoids the required procedure of finding the failure modes and their effect on the individual load points, and results in a significant reduction in computer solution time.