ABSTRACT
Diphenylphenacylsulfonium tetrafluoroborate (DPPS1 BF4–) salt possessing both phenacyl and sulfonium structural units was synthesized and characterized. DPPS1BF4– absorbs light at relatively higher wavelengths. The direct and sensitized initiation activity of the salt in both cationic and free radical photopolymerizations was investigated and compared with that of its analogue triphenylsulfonium tetrafluoroborate (TPS1BF4–). Differential scanning photocalorimetry and conventional gravimetric studies revealed that DPPS1BF4– showed higher efficiency for direct and sensitized photopolymerizations of most of the monomers investigated. Although, principally both homolytic and/or heterolytic cleavage is possible, theoretical studies suggested that homolytic pathway is more favored for the generation of reactive initiating species.
INTRODUCTION
Photopolymerization is currently one of the most important polymerization techniques in wide range of applications such as coatings, adhesives inks, printing, and microelectronics.1–5 While most of the industrial applications of photocuring focus on free radical polymerization techniques, the cationic mode also receives considerable attention in industry and academia mainly due to its insensitivity to oxygen.6 The further growth of such interest is strongly coupled to the development of initiators which fulfill requirements for specific applications. High curing speed, wavelength selectivity, low migration, and solubility are typically important criteria for successful application of initiators in industrial curing processes. Onium salts are known to initiate both free radical and cationic polymerizations.7,8 Among them, iodonium,9–14 pyridinium,11,15 phosphonium,16,17 and sulfonium salts9,14,18,19 are most extensively used as initiators for cationic polymerization. The major drawback of onium type initiators is their low spectral response at high wavelengths.
CONCLUSIONS
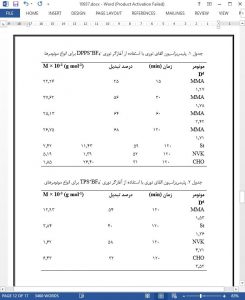
A novel phenacyl-type sulfonium photoinitiator (DPPS1BF– 4) which is capable of initiating both radical and cationic polymerization was synthesized. DPPS1BF– 4 is thermally stable until 198 8C and showed higher absorption characteristics (Supporting Information Figures S3 and S4) with relatively higher polymerization conversions for most of the monomers compared with its triphenyl sulfonium analogue, TPS1BF– 4. Photosensitization studies also revealed that DPPS1BF– 4 gave higher conversions compared with that of TPS1BF– 4 probably due to the additional cationic species formed. CV studies revealed that DPPS1BF– 4 undergoes redox processes more efficiently due to the favorable thermodynamic conditions. Potential coating application of the initiating system was demonstrated by photo-DSC studies using a multifunctional monomer TEGDMA.