Abstract
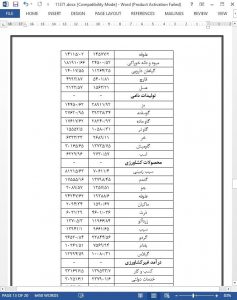
Overexploitation of forest resources continues to pose a severe threat to the environment in Chaprote Valley, Northern Pakistan. Therefore, this study investigates the main determinants of household dependency on forest resources for livelihoods in Chaprote Valley. We collected data randomly from 193 household heads through semi-structured questionnaires. To investigate the dependence of rural households on forest resources, we employed a Logistic regression model. The findings reveal that household’s education level, household size, livestock income and agriculture income significantly affect the dependency of households on forest resources, while other variables seem to be insignificant. The share of forest income to the total household income was 32%, while off-farm income, agriculture income and livestock income were 44%, 13% and 9% respectively. Among all forest products, firewood contributes more to forest income with a share of 47%. Moreover, the study found that an increase in household head’s education, livestock income, agriculture income, off-farm income and own landholding will result in reducing forest dependency. The study concludes that alternate sources of energy, modern agricultural methods, access to higher education, and public awareness about biodiversity are essential for creating a balance between forest dependency and biodiversity conservation.
1. Introduction
Rural livelihoods are highly dependent on environmental sources in developing countries. Most notably, the ecological resources such as timber, firewood, food, and medicines play a vital role in the livelihood of rural people (Angelsen et al., 2014; Babulo et al., 2009; Fikir et al., 2016). The households of rural areas not only utilize forest resources to fulfill their subsistence needs but also generate a significant cash income by trading forest products (Mamo et al., 2007). According to an estimation, 20% of the global population is dependent on forest resources to meet their essential livelihood needs (Cheng et al., 2019). This nexus between forest dependency and biodiversity conservation demonstrates a considerable concern for researchers and academicians to understand the factors of household dependence on forest resources for the sustainability of forest resource management and biodiversity conservation.
4. Conclusion and policy implications
Forest resources play a significant role in rural livelihood, but over-extraction of these resources causes environmental issues for biodiversity conservation and ecosystem. The study aimed to investigate the determinants affecting forest dependency in Chaprote Valley, Northern Pakistan. The primary sources of income in Chaprote Valley include forest income, livestock income, agriculture income, and off-farm income. The results of the study reveal that forest income contributes a significant share of 32% to the total annual household income while off-farm income, agriculture income and livestock income contributes 44%, 13% and 9% respectively. Forest income is the second-largest source of income among all others. Firewood makes a most substantial contribution in forest income with a share of 47%. Furthermore, the negative association of household head’s education, agriculture income, off-farm income and own landholding offers helpful insight for researchers and policymakers. Hence, the results of our study endorse that an increase of off-farm income and agriculture income will result in a lessening of forest dependency in Chaprote Valley.