Abstract
Two complementary architectures, software defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV) are emerging to comprehensively address several networking issues. In this work, we introduce the most embraced virtualization concepts proposed by SDN and NFV architectures. We quantitatively evaluate hardware and energy cost savings with these two SDN and NFV architectures compared to the existing state-of-the-art network 4G hardware technologies.
1. Introduction
Connected devices on the Internet which are commonly known as Internet of Things (IoT) are increasing continuously at an alarming pace. There should be adequate network infrastructure facilities to handle the data explosion. One challenge is that IoT devices are globally distributed. The network infrastructure should be able to reach all these globally distributed devices. This is an enormous challenge and a huge investment in infrastructure by any single service provider. Since users are subscribed to many different service providers, and are globally distributed, it is impossible for each service provider to have its own separate network to serve its own subscribers. As new technology emerges, the hardware becomes quickly obsolete leading to huge recurring costs by each service provider.
5. Conclusion
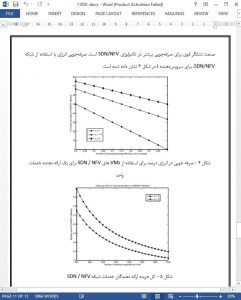
In this work, a cloud based SDN/NFV network was studied and a mathematical model is presented that compares the cost and energy consumption between the SDN/NFV network and a typical 4G network. All key metrics are taken as variable functions to study their effect on the overall cost and energy consumption in the SDN/NFV network. Adhering to the common assumptions in the literature, the proposed model investigates the relative cost and energy consumption for both single service provider and all the service providers in the system as a whole that are involved in SDN/NFV network sharing. By eliminating the possibility of any multiplexing gain, we have still found considerable cost reductions and energy savings in SDN/NFV based networks. The results have substantiated the claims of many gains achievable through successful deployment of networks based on software virtualization.