Abstract
Cloud services are widely used in manufacturing, logistics, digital applications, and document processing. Cloud services must be able to handle tens of thousands of concurrent requests and to enable servers to seamlessly provide the amount of load balancing capacity required to respond to incoming application traffic in addition to allowing users to obtain information quickly and accurately. In the past, researchers have proposed the use of static load balancing or server response times to evaluate load balancing capacity, a lack of which may cause a server to load unevenly. In this study, a dynamic annexed balance method is used to solve this problem. Cloud load balancing (CLB) takes into consideration both server processing power and computer loading, thus making it less likely that a server will be unable to handle excessive computational requirements. Finally, two algorithms in CLB are also addressed with experiments to prove the proposed approach is innovative.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of the Internet, many vendors have started to provide cloud services. More and more services can be obtained in the cloud, and users do not have to do operations on a local computer. All operations are computed on the cloud. When a large number of users attempt to access cloud services, this often causes the server to fail to respond. Determining a method by which to provide users with timely and accurate responses is a subject worthy of advanced study. Several studies have been proposed to evaluate and to develop algorithms and load balancing methodologies for cloudbased applications. It is difficult for a server to deal effectively with the flow of information generated by all of the various enterprises attempting to access it. Excessive flow causes server overload with a subsequent loss of information. A server load balancing mechanism can disperse the transmission of information flow and data operations and can also reduce the probability of increased computational time and loss of information. When one server fails in the cloud, the cloud services can be transferred to another server. Services are therefore non-stop.
6. Conclusions
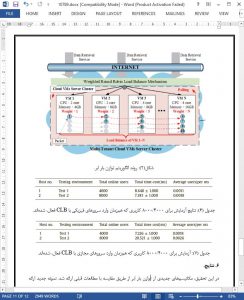
In this study, a new cloud load balancing mechanisms is proposed by comparing previous studies. The proposed new paradigm CLB for load balancing architecture and an algorithm can be applied to both virtual web servers and physical servers. From the experiments for CLB-enabled physical servers and virtual servers, the results show that cloud server performance based on the architecture proposed in this study can balance the loading performance when users logged in at the same time.