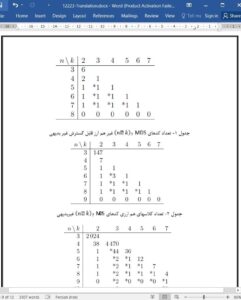
Abstract
A q-ary maximum distance separable (MDS) code C with length n, dimension k over an alphabet A of size q is a set of q k codewords that are elements of An , such that the Hamming distance between two distinct codewords in C is at least n − k + 1. Sets of mutually orthogonal Latin squares of orders q ≤ 9, corresponding to two-dimensional q-ary MDS codes, and q-ary one-error-correcting MDS codes for q ≤ 8 have been classified in earlier studies. These results are used here to complete the classification of all 7-ary and 8-ary MDS codes with d ≥ 3 using a computer search.
1 Introduction
A q-ary code C of length n, and size M is a set of M elements, called codewords, of An , where A is an alphabet of size q. The minimum distance d of a code is the smallest Hamming distance between any two distinct codewords. A code with these parameters is called an (n, M, d)q code. If A is a finite field and C is a vector subspace, then C is called linear. A code that is not linear is called nonlinear. Codes that can be either linear or nonlinear are called unrestricted.