Abstract
The desire to decrease electrical loading by using energy efficient lighting has resulted in a high level of attention to replacing conventional incandescent lamps with compact fluorescent lamps (CFL). In Iran from energy management point of view, people are encouraged by ministry of power to use CFLs. Also after elimination of subsidies, the substantial increase in electric energy price resulted in a high level of penetration of CFLs in electricity grid. CFL is a nonlinear load, therefore it injects harmonic to the network. In past, due to lower application of CFL, these harmonics were ignored, however today by the widespread application of CFLs; these small sources are combined and have high effect on power distribution networks. This paper presents the results of an investigation on the effect of widespread application of CFLs on a real power distribution system of Iran. CFL has some disadvantages that should rectify gradually. However at present great use of this component may cause adverse effects especially on the distribution network. Most of the CFL disadvantages are related to its high level of harmonics. In this paper the interference of the harmonics generated by CFLs to a real distribution network of Iran power grid will be simulated and studied. Since the CFL employed in these network have a relatively poor quality, in this study three samples of the brands which are in wider use in Iran market are selected. The characteristic current of these samples are experimentally determined. After that, CFLs are modeled with considering the attenuation effect. For harmonic mitigation, optimize capacitor placement is done and at the end, Simulation results are discussed.
IV. CONCLUSION
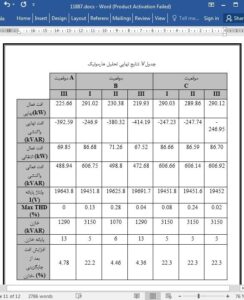
Subsidies allocated to CFLs in Iran have lead to their increasing utilization and accordingly harmonic flowing escalation in power distribution networks. In this paper, the effects of CFLs in Iran’s power network were studied. To have this goal thoroughly accomplished, CFLs were modeled by a narrow consideration into the attenuation effect. The studies were implemented on a practical distribution network in Iran’s power grid. Thereby, simulation results associated with harmonic analysis indicated that there are some sensitive buses in which feeder parameters are more sensitive to load variation. Practically researched, the loads were considered to be a combination of linear and nonlinear loads. Capacitor placement was done afterward. It was indicated that this procedure is directly dependent on the number of CFLs. Moreover, the results demonstrated that the interaction of CFLs and incandescent lamps determines the transformer loss value and THD variation.