Abstract
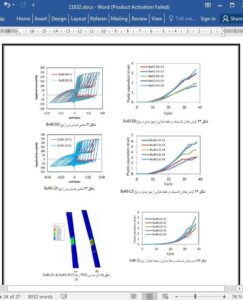
Concentrically braced frames are earthquake resistant systems commonly used in buildings. Seismic behavior of this type of structures is affected by their configurations, brace properties, and brace to gusset plate connections. In this paper, the results of three experiments conducted to investigate the cyclic behavior of concentrically braced frames with braces built-up of double channels are reported. Significant damage was observed in beam to column connections. Large out of plane deformation of braces caused some cracks in the connector welds; however they did not result in fracture. Although large drift was applied to the frames, no brace fracture was observed. Furthermore, experiments showed that the majority of compressive strength in post-buckling state and a noticeable portion of tensile strength originated from frame action. By choosing connector spacing as the main parameter and using finite element models, a parametric study was performed to investigate the effect of this parameter on this type of frames with two different details of brace to gusset plate connections. It is observed that reducing the connector spacing increases the inelastic strain demand in braces and decreases it in gusset plates. However, gusset plates, which accommodate 2t linear clearance, are less dependent on connector spacing, compared to those accommodating 6t elliptical clearance. It seems that the limitations of slenderness ratio of individual section, stipulated in current seismic provisions, need further study.
1. Introduction
Concentrically braced frames, CBFs, are frequently used as a structural system to resist earthquake loading. High strength and stiffness as well as economic consideration have attracted engineers to this structural system. Seismic behavior of this type of frames is affected by their configurations; brace properties such as slenderness, section geometry, compactness, and details of brace to gusset plate connections. In the past, different studies have been undertaken on this kind of frames, which can be classified in three distinct categories. In the first category, the seismic behavior of CBFs have been investigated with respect to their configurations, e.g. frames with diagonal, X, and chevron braces or those with super-X. In the second category, details of connection of brace to gusset plates have been the main parameters of interest. The third category of research has concentrated on the effects of properties of the brace section such as geometry, slenderness ratio, and width to thickness ratio on the seismic behavior of CBFs. In the following paragraphs, some of the researches falling in the second and third categories are reviewed briefly.