Abstract
Sustainable construction practices require cementitious materials with high strength that is strongly dependent upon the nature of binding materials and pore structure. The physico-chemical properties of these materials can be tailored suitably by preferential substitution of cement by materials having comparatively small particle size resulting in improved pore structure. This study is aimed to investigate strength and microstructure of the preferentially substituted cement mortars with incorporation of microsilica (MS), nanosilica (NS) and their combined use at 3, 7 and 28 days of curing. The substituent MS (5.0–20%) and NS (0.5–1.25%) have been used at a water binder ratio of 0.5. The specimens were analyzed for the fresh (consistency, setting time, flow) and hardened (compressive and split tensile strength) properties and a correlation between compressive and split tensile strength was obtained. Mortar containing NS was found to develop better strength as compared to the mortar containing MS. The optimum usage of MS with incorporation of NS was further found to increase the strength of mortar significantly. SEM-EDX was used for the analysis of the microstructure of the specimens and the correlation between Ca and Si content was used to analyze the cement matrix. The findings show that the optimized usage of micro and nano silica can give beneficial effects to improve the fresh properties as well as strength with dense microstructure.
1. Introduction
Cementitious materials are the composite materials produced from Portland cement with paramount importance in all the construction fields due to their extensive applications. Day-by Day increasing world population and tremendous technological & industrial advancement leading to massive infrastructure requirement has further increased the demand of cement [1]. The production of cement and fine aggregates is not only highly energy intensive, but also pose a threat to the environment due to release of harmful pollutants including particulates and greenhouse gases [2].
3. Conclusion
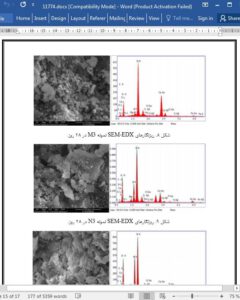
The study of effect of preferential substitution of cement by MS and/or NS on fresh as well as hardened properties & microstructure of cement mortars in comparison to control mix has been carried out. The consistency, initial and final setting time of the specimens were found to increase while the flow was found to decrease in content of MS as well as that of NS but the effect was more pronounced in case of ternary blends. An increase in compressive and split tensile strength was obtained with increasing content of MS and NS from 5.0% to 15% and from 0.5% to 1.0% respectively along with a slight reduction in strength afterwards. The results were confirmed with SEM-EDX analysis with profound decrease in Ca/Si ratio accordingly. This decrease in strength was because of the reduction in homogeneity of the cement matrix at higher content of MS while the decrease in strength at higher content of NS was attributed to the agglomeration of nano particles at higher content in the cement matrix. SEM-EDX analysis confirmed the loss of pozzolanic activity of MS and NS at higher content due to agglomeration and friction among particles.