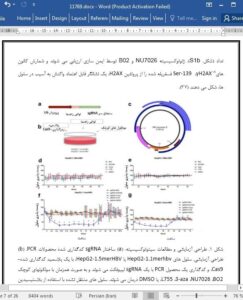
Chronic hepatitis B is a severe liver disease caused by hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA), a super-spiralized, double-stranded form of the HBV genome, is the major determinant of viral persistence. CRISPR/Cas9 nucleases have been recently shown to introduce doublestranded DNA breaks into HBV cccDNA. The inficted damage results predominantly in erroneous repair of cccDNA by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ). NHEJ has been suggested to enhance anti-HBV activity of CRISPR/Cas9 and increase cccDNA mutation. In this study, we assessed anti-HBV activity of CRISPR/Cas9 and cccDNA repair outcomes in an altered NHEJ/HR environment. NU7026, a strong inhibitor of NHEJ, prevented CRISPR/Cas9-mediated degradation of cccDNA and resulted in frequent on-target deletions. We conclude that CRISPR/Cas9 is a highly efective tool to degrade cccDNA and frst demonstrate that inhibiting NHEJ impairs cccDNA degradation.
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) chronically infects 250 million people worldwide, and more than a million people die from consequences of chronic hepatitis B (CHB), mainly cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)1–3 . HBV belongs to the family Hepadnaviridae. Te viral genome of the enveloped HBV particle comprises a circular, partially double-stranded DNA that is synthesized from an RNA intermediate using a reverse transcriptase. Upon entry, HBV virions are uncoated, and relaxed circular DNA is transported into the nucleus where it is repaired to form covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA). cccDNA is the key component of that HBV life cycle that serves as a template for transcription of all viral mRNAs including pre-genomic RNA (pgRNA)4–6
Next-generation sequencing. Regions targeted by CRISPR/Cas9 and potential off- arget regions were amplifi d using pairs of specific primers and Q5 polymerase. Amplicons were gel-purifi d and extracted using Qiagen gel extraction kit, quantifi d with a Qubit 2.0 Fluorometer (Life Technologies), and pooled in equimolar ratios. Adapters for Illumina sequencing were then attached. Libraries were sequenced with 250 paired-end reads using the MiSeq instrument (Illumina). FASTQC sofware and Geneious sofware were used for quality assessment, reference alignment, discarding low-quality reads/nucleotides, and calculating substitutions and indels. Per-base sequence quality and per-sequence quality scores in all groups were >30.