Abstract
Owing to the development of highly efficient electric power converters, the number of studies on the construction of low-voltage DC (LVDC) systems is gradually increasing. To use LVDC distribution systems, voltage regulation methods to compensate for the voltage drop and to limit the voltage unbalance are essential. In a bipolar LVDC distribution system, a voltage drop and voltage unbalance could occur because of the load current and the variation in the amount of power supplied to the poles. However, not enough research has been conducted on voltage regulation methods for LVDC distribution systems. To reduce the voltage drop and the voltage unbalance, this paper proposes a voltage regulation method based on the neutral to line drop compensation (NLDC) method, which employs a modified LDC to calculate the sending-end reference voltage. In the NLDC method, the neutral current and neutral line impedance are taken into consideration to compensate for the neutral line potential fluctuation and voltage drop on the pole. The next sending-end voltage is determined by checking the voltage unbalance factor, and it is adjusted to maintain it within the allowable voltage unbalance factor. A voltage regulation algorithm and a bipolar LVDC system model are implemented using ElectroMagnetic Transients Program.
I. INTRODUCTION
TO reduce the energy losses, various studies on improving the power efficiency have been performed worldwide. In this paper, the low-voltage DC (LVDC) distribution system is investigated as a solution to the power efficiency problem, because of its many advantages. With a dc distribution system, power conversion within the appliance can be avoided and losses reduced. Moreover, the LVDC system is well suited for connection of various renewable energy systems such as photovoltaic and fuel cells producing DC power by reducing the number of conversions: DC/DC/AC to DC/DC conversion. In addition, the efficiency of the microturbine and variable speed wind turbine that produce the AC power can be improved in an LVDC system by reducing the number of conversions: AC/DC/AC to AC/DC conversion [1]–[6].
VI. CONCLUSION
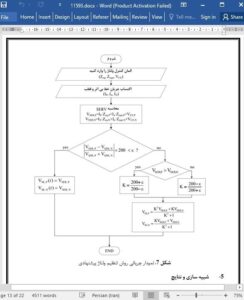
This paper proposes a novel technology to compensate for the voltage drop and voltage unbalance in a bipolar LVDC distribution system. The NLDC method, which takes the neutral line current and neutral line equivalent impedance into consideration, compensates for the pole line voltage drop and reduces the neutral potential fluctuation. In order to verify the proposed method, a bipolar LVDC distribution system is modeled, and a boost balancer is implemented by using EMTP. In addition, the algebraic least mean square is used to determine NLDC parameters such as the SERV and the line current by using MATLAB. The simulation results confirm that the proposed method is effective in compensating for the voltage drop and in mitigating the voltage unbalance in bipolarLVDC distribution systems. The simulation results show that the smallest PI is obtained by the NLDC method, and not by the conventional methods. This is because the neutral potential fluctuation largely depends on the neutral current generated by the load unbalance condition. Moreover, it is verified that the NLDC method is useful in mitigating the voltage unbalance. In conclusion, the proposed method contributes to the improvement of voltage regulation and the effective mitigation of the voltage unbalance in bipolar LVDC distribution systems by providing better performance than the existing methods.