Abstract
In this work we propose the GLRT-MP algorithm which combines compressed sensing techniques and classical detection theory and explores its application to sparse arrays. Sparse arrays are large undersample arrays with nonuniform spacing that provides high resolution at the cost of high sidelobes. Compressed sensing techniques are able to minimize the undesired effects of the large array, while classical detection theory provides a way to perform detection while maintaining a desired false alarm probability. We provide analysis of the GLRT when the noise power is known and unknown, the latter which will allow one to design a CFAR radar. We provide numerical results to verify our results.
I. INTRODUCTION
It is well known that a uniform linear array (ULA) with half wavelength spacing ensures the absence of grating lobes in the visible region of the array pattern. ULAs also produce low sidelobes, a desirable trait during the beamforming stages of target detection. In contrast, sparse arrays with large, nonuniform inter-element spacing produces large sidelobes but achieve higher resolution due to the large aperture [16]. However, due to the large sidelobes, the beamformer often experience false peaks, which increases the probability of false alarm.
In recent years, compressive sensing (CS) techniques tailored for sparse localization frameworks [4], [8] were shown to be able to cope with the spatial undersampling of sparse arrays [5]. This exciting result enables the radar designer to implement large undersampled arrays without needlessly increasing the false alarm probability. However, much of the literature in CS techniques addressing localization of sparse targets (e.g. [9], [10], [11]) fails to explain how CS techniques affect parameters of interest to radar, specifically the probabilities of false alarm and detection.
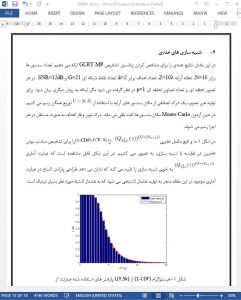
V. CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we developed a GLRT for multiple targets when the noise power is known and provided the false alarm and detection probabilities. We then build upon the known noise case and develop a CFAR detector for multiple targets and provide the false alarm and detection probabilities. We then propose the GLRT-MP algorithm, a detector that combines matching pursuit concepts and the GLRT derived in this paper. Numerical results show that the analytical expressions derived in this paper closely match the simulation results and outperforms the conventional beamformer.