Abstract
Quality cost control is one of the most important aspects in the development of a quality management system. This paper presents a method for the estimation of quality cost that aims to take into account the so-called hidden quality costs, which are typically unobserved or unknown. Although this is a subject that has already been approached in other studies, subjectivity and uncertainty are not included in their formal approach, which any attempt to address hidden quality costs should include. Our methodology begins by observing the position each business occupies in Crosby's Quality Management Maturity Grid. Obtaining the stage index on the basis of the experts' opinions permits the valuation of the company's membership for each of the stages of Crosby's Maturity Grid. The application of Crosby's corrector coefficient to an adequate weighting of the stage index makes it possible to obtain the fuzzy number quality cost. The measures obtained and their short-term predictions enable us to know the situation at all times and act accordingly, establishing precise corrective plans that will correct tendencies and make continuous improvement possible.
1. Introduction
Measuring and reporting quality cost is an important step in a quality management program [1]. In this paper, we will develop a methodological proposal that mainly aims to facilitate the acquisition, and then the analysis and short-term prediction of reliable quality cost values.
Ever since Juran [2] introduced the concept of quality costs in the 50s, the subject has spurred an interest in many authors. Among the many existing definitions, in our opinion the one standing out because of its clarity is that by Campanella [3], who considers quality costs “the total of the costs incurred by investing in the prevention of non-conformances to requirements, appraising a product or service for conformance to requirements and failure to meet requirements.” This means, as Juran and Godfrey [4] indicated, they are the costs that would disappear if there were no possibility of making mistakes.
6. Conclusions
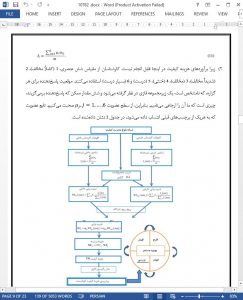
One of the main problems with quality cost estimation in businesses is the existence of certain elements that are called hidden quality costs, whose quantification is at best uncertain and subjective. This is why a unique tool has been developed, based on the position each business occupies on Crosby’s reputed quality Management Maturity Grid, which allows a company’s calculated quality costs to be transformed into fuzzy numbers.
In particular, obtaining the stage index on the basis of the experts’ opinions permits the valuation of the company’s membership for each of the stages of Crosby’s Maturity Grid. The application of Crosby’s corrector coefficient to an adequate weighting of the stage index makes it possible to obtain the maximum costs the company could incur (maximum cost) based on initial estimations (calculated costs), thus permitting the construction of the TFN quality cost.