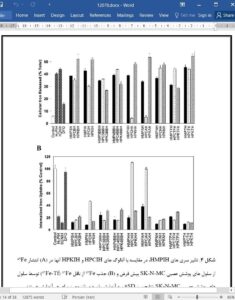
The design of novel Fe chelators with high Fe mobilization efficacy and low toxicity remains an important priority for the treatment of Fe overload disease. We have designed and synthesized the novel methyl pyrazinylketone isonicotinoyl hydrazone (HMPIH) analogs based on previously investigated aroylhydrazone chelators. The HMPIH series demonstrated high Fe mobilization efficacy from cells and showed limited to moderate antiproliferative activity. Importantly, this novel series demonstrated irreversible electrochemistry, which was attributed to the electron-withdrawing effects of the noncoordinating pyrazine N-atom. The latter functionality played a major role in forming redox-inactive complexes that prevent reactive oxygen species generation. In fact, the Fe complexes of the HMPIH series prevented the oxidation of ascorbate and hydroxylation of benzoate. We determined that the incorporation of electron-withdrawing groups is an important feature in the design of N,N,O-aroylhydrazones as candidate drugs for the treatment of Fe overload disease.
Introduction
The synthesis and design of novel iron (Fe) chelators is of great importance for the treatment of Fe-loading diseases such as β-thalassemia major.1–5 This is due to the fact that treatment with the clinically used chelator, desferrioxamine (DFOa ; Figure 1A), suffers many drawbacks that are partly caused by its high hydrophilicity.5,6 This leads to poor absorption from the gastrointestinal tract, which necessitates subcutaneous administration for 12–24 h/day, 5–6 times/week to achieve a negative Fe balance.7 In addition, a third of all patients treated with DFO experience swelling and pain at the injection site.8,9 Cumulatively, these problems lead to poor patient compliance.