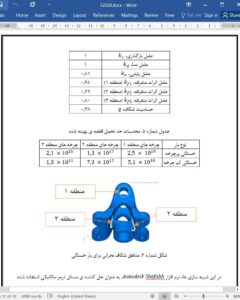
Abstract
Additive Manufacturing (AM) is a new generation manufacturing method and AM is using digital CAD data directed to the machine to manufacture. AM is therefore regarded as a direct digital manufacturing method. This research work presents the methodology for designing critical aerospace parts used under fatigue conditions for AM. Selected fatigue critical aerospace part was topologically optimized then re-designed for manufacturability. With this optimization study, 45 % mass saving was obtained while mechanical requirements were satisfied. Manufacturing simulations for thermal distortions are covered and the optimized part was manufactured with laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF) and secondary operations were applied.
1. Introduction
The aviation and space industries are the most critical sectors where additive manufacturing (AM) is most potentially used and the total revenues from AM are expected to gradually increase over the next 20 years [8]. Such an extraordinary trend of AM is of course the AM Technologies is regarded as the novel direct digital manufacturing (DDM). DDM defines as the de-centralized manufacturing of the parts in accordance with proper qualification and certification [5]. Another reason behind the extensive usage of AM can be correlated with the flexibility in design. Owing to the manufacturing freedom of the AM processes, more complex geometries having lighter and stiffer properties can be designed and manufactured. In design for AM, topology optimization (TO) method has been preferred due to its significant role in weight reduction