Abstract
The simulation of crack propagation processes in rock engineering has been not only a research hot spot among scholars but also a challenge. Based on this background, a new numerical method named improved kernel of smoothed particle hydrodynamics (IKSPH) has been put forward. By improving the kernel function in the traditional smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) method, the brittle fracture characteristics of the base particles are realized. The particle domain searching method (PDSM) has also been put forward to generate the arbitrary complex fissure networks. Three numerical examples are analyzed to validate the efficiency of IKSPH and PDSM, which can correctly reveal the morphology of wing crack and the laws of crack coalescence compared with previous experimental and numerical studies. Finally, a rock slope model with complex joints is numerically simulated and the progressive failure processes are exhibited, which indicates that the IKSPH method can be well applied to rock mechanics engineering. The research results showed that IKSPH method reduces the programming difficulties and avoids the traditional grid distortion, which can provide some references for the application of IKSPH to rock mechanics engineering and the understanding of rock fracture mechanisms.
1. Introduction
Rock is a typical anisotropic material, which contains large amounts of inherent defects with relatively lower strength. These defects include faults, fissures, joints, holes, interlayers and so on, which makes rock exhibit the characteristics of heterogeneity, non-linearity, and strong discontinuity [1]. Furthermore, under complex multi-field coupling conditions [2], the rock structures may fail due to these defects. Therefore, how to correctly describe the discontinuous characteristics of rock masses has been a hot but difficult problem in recent years.
6. Conclusions
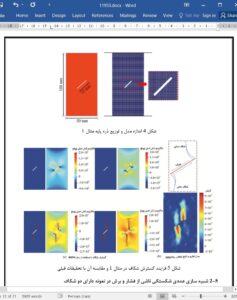
(1) A new numerical method named improved kernel of smoothed particle hydrodynamics (IKSPH), which is aimed at modeling the brittle fracture of rock masses, has been proposed in this paper. Compared with previous studies, there is no need to reduce the stiffness of the base point or map the stress to the stress bond between different base particles, which has reduced programming difficulties. Meanwhile, the particle domain searching method (PDSM) has also been put forward to generate complex fissure networks.