Abstract
Background Vaccinia virus was widely used in the World Health Organization’s smallpox eradication campaign and is currently a promising vector for gene therapy owing to its unique characteristics. Vaccinia virus can selectively replicate and propagate productively in tumor cells, resulting in oncolysis. In addition, rapid viral particle production, wide host range, large genome size (approximately 200 kb), and safe handling render vaccinia virus a suitable vector for gene therapy.
Materials and methods Cancer vaccines and gene therapy are being studied in clinical trials and experiment researches. However, we put forward unique challenges of optimal selection of foreign genes, administration and modification of VACV, personalized medicine, and other existing problems, based on current researches and our own experiments.
Conclusion This review presents an overview of the vaccinia virus from its mechanisms to medical researches and clinical trials. We believe that the solution to these problems will contribute to understanding mechanisms of VACV and provide a theoretical basis for clinical treatment.
Background
Cancer treatment strategies are currently a global concern. Approximately 7 million individuals worldwide die of malignant tumors annually; this number is predicted to increase to 12 million in 2030. Primary cancer treatment strategies include surgical treatment, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. However, these traditional treatment methods have limitations. Through traditional surgical treatment, tumor tissue can be rapidly and directly resected; however, incomplete resection may lead to the persistence of residual tumors. Furthermore, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are not target-specific; along with tumor cells, these methods also eliminate healthy immune cells, thereby lowering patient immunity. Therefore, new targeted therapeutic strategies are warranted to overcome these limitations in cancer treatment. Advancements in genetic engineering have facilitated the use of viral vectors for cancer gene therapy (Chan and Mcfadden 2014). This novel treatment strategy for malignant tumors delivers foreign genetic materials into tumor cells via viral vectors, thereby potentially rectifying congenital metabolic abnormalities, compensating for gene deletion, or facilitating a novel function.
Conclusion
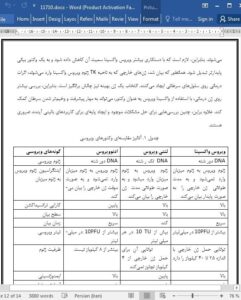
Currently, most studies on oncolytic viruses use adenovirus and lentiviral vectors as models; however, the unique advantages of the vaccinia virus make it a suitable vector for gene therapy (Table 1), thereby bringing hope to patients with different cancer types. Comprehensive and individualized approaches are suggested for the treatment of different patients with cancer. Therefore, there is the need to modify the vaccinia virus to reduce its toxicity level and to make it a more stable expression virus vector. As established, foreign genes integrated into the TK region of the vaccinia virus exert therapeutic effects on cancer cells. The selection of an optimal gene is also challenging. Therefore, further investigations on gene therapy, using the oncolytic vaccinia virus as a vector, could help prevent the progression and deterioration of cancer. Moreover, such investigations are very necessary for solving the existing problems, and provide the basis for future clinical applications.