Abstract
Resource scheduling and energy consumption are the two of most significant problems in cloud computing. Owing to the scale and complexity of various resources, it is often difficult to conduct the theoretical analysis of the performance and power consumption of scheduling and resource provisioning algorithms on Cloud testbeds. Thus, simulation frameworks are becoming important ways to complete evaluation. CloudSim is one of the most popular and powerful simulation platforms for cloud computing. However, it requires much improvement to enable CloudSim to perform multi-resource or energy-aware simulations. To overcome this problem, we have extended CloudSim with a multi-resource scheduling and power consumption model, which allows more accurate valuation of power consumption in dynamic multi-resource scheduling. Extensive experiments on six combinations of task assignment algorithms and resource allocation algorithms demonstrate the powerful functionality and superior convenience of the extended CloudSim, MultiRECloudSim. Different task assignment and resource scheduling policies will bring about very different energy cost. We could easily repeat the experiment to find out the efficiency and the power consumption of the algorithms under diverse arguments with MultiRECloudSim.
1 Introduction
Cloud computing [2,6,11,31] has rapidly attracted more and more attention in both academic and industry community. In cloud computing, server consolidation is an approach to the efficient usage of server resources in order to reduce the total number of servers that user requires [34]. The growth of server consolidation is owing to virtualization technology which enables multiple VMs to share the physical resources of a computer. The total resources of VMs shared the same server must not exceed that of the server while the number of servers is required to be as small as possible. Server virtualization provides technical ways to consolidate multiple servers bringing about increased utilization and energy saving. As for resource scheduling for tasks, Resource provisioning consists of two provisioning plan for allocating resources in cloud. These are long term Reservation plan and short term On-demand plan [9].
7 Conclusions
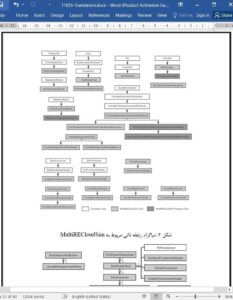
Owing to the support for flexible, scalable, efficient, and repeatable evaluation of resource scheduling and allocation policies for different applications, using simulation tools such as CloudSim is becoming more and more popular. Fast evaluation of scheduling and resource allocation algorithms within data centers becomes available. Therefore, we present a novel CloudSim-based simulation framework which supports the modeling of multi-resource scheduling and power consumption to make up the shortcomings of CloudSim in these aspects. Cloud simulation experiment with MultiRECloudSim has obvious priorities. (1) We can change configuration of host and power models of resources easily, and test the effect of algorithm under different parameters. (2) We simply simulate tasks that demand multi kinds of resources and define different resource allocation algorithms with fine-grained evaluation. (3) We could seamlessly switch static load and dynamical load experiment, which makes it able to simulate more actual scenes. (4) We support the power simulation of multi-resources. It is more accurate compared with single resource CPU power simulation. Additionally, in our work, we compare multiple combinations of task assignment algorithms and CPU allocation algorithms with each other from the aspects of time, power consumption and SLA violation. The result helps us to know more about the efficiency, power consumption and service quality’s performance of the scheduling algorithms. Our proposed Main Resource Task Balance assignment algorithm raise the data center’s resource utilization effectively and improve the throughput as well as service quality.