Abstract
This paper investigates the determinants of trust in banking networks and, thus, identifies several forces determining the stabilizing effect of networks. Using a unique dataset of 249 German savings banks, the empirical results show that intense interaction with central coordinators supports trust-building within the network. Larger banks and banks with strong competitive standing and high income invest less in a deeper relationship with the network. Moreover, bank's own trustworthiness is a relevant component in building trust. The banks are more willing to trust if they believe that they can influence the banking group's decisions. These findings may help to explain how banking networks can function well even in periods of financial crisis.
1. Introduction
The financial crisis has revealed a strong need for understanding the role of trust in complex and interlinked networks. Market participants, politicians and researchers have once more realized that the level of trust within a system or a network of financial institutions is important for the stability of the network. This paper is an empirical investigation of the circumstances under which trust in network mechanisms is created and maintained and of how banking networks can function well even in periods of financial crisis.
Bank crises have been studied extensively, and various sources of systemic risk have been identified. The most important source of systemic risk is contagion. The common perception is that interlinkages may create a risk of financial contagion (see e.g. Brusco and Castiglionesi, 2007; Dasgupta, 2004). However, economic theory shows that the risk of contagion is dependent on the precise pattern of interbank linkages.
7. Conclusion
In this paper, I investigated the determinants of trust in banking networks and argued that the level of trust is important for the stability of a system, drawing guidance from the recent financial crisis. The collapse in trust played a crucial role in the recent crisis. Therefore, understanding the determinants of trust in banking networks is the first step toward gaining a better understanding of modern financial systems.
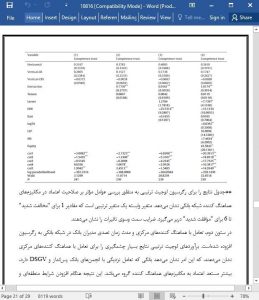
Using the German Savings Banks Finance Group as a concrete case to investigate the determinants of competence trust in banking networks I have identified several forces determining the stabilizing effect of banking networks.