Abstract
Lightning stroke causes a current injection into transmission lines at the point of contact. The lightning performance can be difficult to understand without using simulation programs. PSCAD a powerful software was selected to develop the appropriate data required to investigate this phenomena.
In this paper, two points along transmission line are selected for studying voltage–time (V–t) characteristics when any of those points is subjected to lightning strokes separately. The first assumed point is taken when lightning current is injected to the shielding wire at the top of the transmission tower, while, the other assumed point is taken when surge current is injected to the shielding wire at maximum sag location in the mid-span between two towers. The sag of transmission line has been newly developed and simulated using PSCAD.
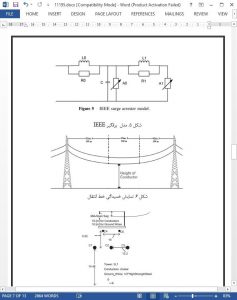
Both transmission line containing sag as well as lightning injection current are modeled. Fast transient of flashover as well as back flashover occurrence is investigated. The results revealed that the sag of transmission line has considerable influence on flashover and induced voltages across line insulators and phase lines as well. The influence of connecting surge arrester in substations is investigated. A proper transmission line arrester (TLA) is designed in order to minimize the occurrences of overvoltages due to flashover and consequently back flashover across insulators.
1. Introduction
One of the natural sources of transient overvoltage in the power system is lightning strokes. Lightning stroke is an impulsive transient variation which is unidirectional in polarity (positive or negative). Overhead transmission line is the most part subjected to the lightning phenomena. Transmission lines are protected from the direct lightning by shield wires. The lightning current injection to shield wires or tower body will cause induced voltage across insulators and phase lines (Bollen et al., 2005).
In previous works, most researchers had studied several parameters that affect the lightning performance on transmission system. The common parameters of lightning are: front time, tail time, peak lightning current, tower geometry, footing resistance, corona, flashover, etc (Chowdhuri, 2001; Talib et al., 2012; Yadee and Prem, 2007).
4. Conclusion
In this paper, the effect of lightning current injected at the top of transmission tower as well as at maximum sag location of 500 kV transmission system is simulated with and without using surge arresters. The obtained results report that the sag of transmission line has an obvious effect on V–t characteristics caused by lightning surges and consequently transient overvoltage protection.