Abstract
This article provides a review of Blood Oxygen Level Dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging (BOLD fMRI) applications for presurgical mapping in patients with brain tumors who are being considered for lesion resection. Initially, the physical principle of the BOLD effect is discussed, followed by a general overview of the aims of presurgical planning. Subsequently, a review of sensorimotor, language and visual paradigms that are typically utilized in clinical fMRI is provided, followed by a brief description of studies demonstrating the clinical impact of preoperative BOLD fMRI. After this thorough introduction to presurgical fMRI, a detailed explanation of the phenomenon of neurovascular uncoupling (NVU), a major limitation of fMRI, is provided, followed by a discussion of the different approaches taken for BOLD cerebrovascular reactivity (CVR) mapping, which is an effective method of detecting NVU. We then include one clinical case which demonstrates the value of CVR mapping in clinical preoperative fMRI interpretation. The paper then concludes with a brief review of applications of CVR mapping other than for presurgical mapping.
INTRODUCTION
Blood Oxygen Level Dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging (BOLD fMRI) is a brain mapping technique using deoxyhemoglobin contained in the blood vessels as an endogenous contrast agent to produce functional activation maps[1].
Neural activation induces a transient increase in regional oxygen extraction from the blood that is coupled with a much larger increase in cerebral blood flow (CBF) and cerebral blood volume (CBV). This influx of oxygenated hemoglobin results in a net decrease in regional deoxyhemoglobin concentration. This drop in paramagnetic deoxyhemoglobin concentration leads to an increase in the magnetic relaxation times T2 and T2*. The mapping of eloquent areas is thus obtained by acquiring T2 or T2*- weighted images consecutively while the subject is at rest or performing a task, and detecting the signal increase related to the local reduction of deoxyhemoglobin concentration accompanying the functional activation relative to baseline.
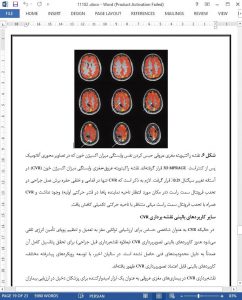
OTHER CLINICAL APPLICATIONS OF CVR MAPPING
While CVR is considered a sensitive indicator for assessing the brain’s ability to dynamically adjust its energy supply, the clinical applications of CVR mapping (aside from presurgical mapping) are yet to reach their full potential, mainly due to technical constraints. In recent years, with the development of various advanced approaches, viable clinical applications of CVR mapping have emerged.
CVR mapping in cerebrovascular disease is emerging as a promising tool for clinicians involved in the evaluation of patients at risk for stroke. A few studies have been reported using hypercapnia induced BOLD MRI signal response to probe CVR in patients with arterial steno-occlusive diseases such as carotid artery stenosis[55,71,72]. For example, a patient with right middle cerebral artery occlusion and Moyamoya phenomenon secondary to aplastic anemia showed paradoxical CVR values in the right middle cerebral artery territory in the cortex[55].