Abstract
This paper evaluates the scheduling problem for energy hub system consisting of wind turbine, combined heat and power units, auxiliary boilers, and energy storage devices via hybrid stochastic/information gap decision theory (IGDT) approach. Considering that energy hub plays an undeniable role as the coupling among various energy infrastructures, still it is essential to be investigated in both modeling and scheduling aspects. On the other hand, penetration of wind power generation is significantly increased in energy infrastructures in recent years. In response, this paper aims to focus on the hybrid stochastic/IGDT optimization method for the optimal scheduling of wind integrated energy hub considering the uncertainties of wind power generation, energy prices and energy demands explicitly in a way that not only global optimal solution can be reached, but also volume of computations can be lighten. In addition, by the proposed hybrid model, the energy hub operator can pursue two different strategies to face with price uncertainty, i.e., risk-seeker strategy and risk-averse strategy. This method optimizes energy hub scheduling problem in uncertain environment by mixed-integer nonlinear programming. This formulation is proposed to minimize the expected operation cost of energy hub where different energy demands of energy hub would be efficiently met. The forecast errors of uncertainties related to wind power generation and energy demands are modeled as a scenario, while an IGDT optimization approach is proposed to model electricity price uncertainty.
A. Motivation and Problem Description
As the penetration of intermittent renewable energy resources increase substantially in energy infrastructures, renewable generation intermittency and variability causes big challenges on energy infrastructure scheduling. Among the renewable energy resources, wind generation assigns a remarkable portion of the renewable generations, due to energy balance efficiency and low marginal operating costs [1]. However, one possibility to smooth the effect of limited predictability and uncertainty of wind generation as well as convert potential possibility of these kinds of resources into actual solutions is coordinating different energy infrastructures [2]. An energy hub can be defined as an interface between various energy infrastructures such as electricity and natural gas networks [3-5]. On the other hand, an energy hub can reduce consumption of primary energy, the sequential pollutant emissions and the cost of energy consumption [4, 6]. Towards the goal of supplying energy demands in an economical, environmentally friendly and reliable way, planning, operation, and energy management of energy hub systems have been extensively investigated recently. An essential problem of the associated planning and scheduling tasks is to consider the effect of uncertainties associated with wind power, energy demands and energy market tariffs so that total energy demands can be served, while the cost of serving energy to customers is minimized.
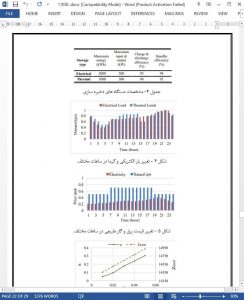
IV. CONCLUSION
In this paper, a scheduling strategy for an energy hub system based on hybrid stochastic/IGDT optimization is proposed. The uncertain outputs of wind generation and energy demands are modeled via scenarios, while an IGDT optimization is implemented to find an interval for electricity price to study the robustness and opportunity functions. By the proposed hybrid model, the energy hub operator can track risk-averse and risk-seeker strategies to face with price uncertainty. By implementing the hybrid stochastic/IGDT optimization method for the optimal scheduling of wind integrated energy hub, the computation burden of the problem is decreased. Finally, the numerical results obtained from the studied cases verified the appropriateness and usefulness of the proposed method, where it is shown that by applying different strategies such as risk-averse and risk-seeker strategies provided by hybrid stochastic/IGDT model grants additional degree of freedom in deregulated energy markets for energy hub operator.