Abstract
Nonlinear free vibration analysis of curved double-walled carbon nanotubes (DWNTs) embedded in an elastic medium is studied in this study. Nonlinearities considered are due to large deflection of carbon nanotubes (geometric nonlinearity) and nonlinear interlayer van der Waals forces between inner and outer tubes. The differential quadrature method (DQM) is utilized to discretize the partial differential equations of motion in spatial domain, which resulted in a nonlinear set of algebraic equations of motion. The effect of nonlinearities, different end conditions, initial curvature, and stiffness of the surrounding elastic medium, and vibrational modes on the nonlinear free vibration of DWCNTs is studied. Results show that it is possible to detect different vibration modes occurring at a single vibration frequency when CNTs vibrate in the out-of-phase vibration mode. Moreover, it is observed that boundary conditions have significant effect on the nonlinear natural frequencies of the DWCNT including multiple solutions.
1. Introduction
After the discovery of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) by Iigima [1], considerable attention has been devoted to carbon nanotubes (CNTs), since they have the ability to revolutionize critical technologies owing to their remarkable physical, mechanical, and electrical properties [2]. These extraordinary properties made CNTs as perfect materials for a wide range of applications [3–5]. CNTs can be efficiently utilized as nano-pipes used in fluid transport and drug delivery systems [6–8]. Also, CNTs have potential applications in nano-actuators, nano-motors, and nano-sensors [9–12].
7. Conclusion
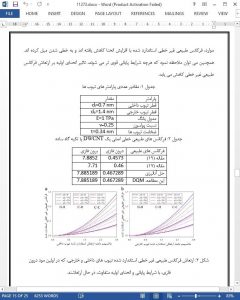
In this paper, nonlinear free vibration of a curved DWCNT embedded in elastic medium is studied by using differential quadrature method (DQM) where in addition to geometric nonlinearity, interlayer vdW force nonlinearity is also included. The effect of nonlinearities, end conditions, initial curvature, stiffness of the surrounding elastic medium, and vibrational modes on the nonlinear free vibration of DWCNTs is studied in detail.
Results show that nonlinear natural frequency increases as vibration amplitude increases in the presence of only geometric nonlinearity for all the type of end conditions. Moreover, it is observed that multiple solution at same vibration amplitude can exist due to interaction of nonlinear in-phase and out-of-phase vibration modes.