Abstract
Since National Health Insurance program formally went into effect in March 1995 in Taiwan, the residents enjoy high quality but relatively cheaper medical care compared with the most developed countries. To manage a hospital successfully, the important goals are to attract and then retain as many patients as possible by meeting potential demands of various kinds of the patients. This study first conducted the survey based on SERVQUAL model to identify seven major criteria from patients’ or their families’ viewpoints at Show Chwan Memorial Hospital in Changhua City, Taiwan. When the key criteria were found, the second survey developed for applying decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL) method was issued to the hospital management by evaluating the importance of criteria and constructing the causal relations among the criteria. The results show that trusted medical staff with professional competence of health care is the most important criterion and mutually affects service personnel with good communication skills, service personnel with immediate problem-solving abilities, detailed description of the patient’s condition by the medical doctor, and medical staff with professional abilities. Therefore, trainings on communication skills and problem-solving abilities would result in positive interaction for patients to trust medical staff. When the trusted medical staff provides professional competence of health care to patients, satisfaction would be increased.
1. Introduction
Before March 1995, there were 13 independent public medical insurance systems featuring distinct premiums and benefits to different segments of the society. This public medical insurance network only covered 60% of the population but the remaining 40%, mostly senior citizens, children, and unemployed workers, were uninsured (source: http://www.nhi.gov.tw/english/webdata.asp? menu=11&menu_id=290&webdata_id=2964). In order to provide health care to all citizens in Taiwan, the National Health Insurance program executed by Bureau of National Health Insurance was launched by the government, which is a mandatory, single-payer social health insurance system based on the principle that each person should have equal access to health care services by providing universal coverage, health care of acceptable quality, comprehensive benefits, and convenient access to treatment with low premiums and health care expenditures. Under such program, citizens are able to freely choose health care providers and medical institutions. The satisfaction rating by the citizens has been very consistent by more than 70%. More importantly, the National Health Insurance program was highly recognized and praised by international media, such as Dissent, US political magazine, in the winter 2008 edition with the title of ‘‘Health care in Taiwan: why cannot the United States learn some lessons?” and Nobel Laureate and New York Times columnist Paul Krugman, who praised Taiwan’s health care system that had expanded coverage without a major increase in health expenditures in a November 7, 2005 column called ‘‘Pride, prejudice, insurance” (source: http://www.nhi. gov.tw/english/webdata.asp?menu=11&menu_id=290&webdata_ id=2972).
4. Conclusions
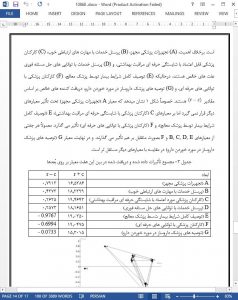
This study first conducted the survey based on SERVQUAL model to identify seven major criteria among 22 criteria from the patients’ or their families’ viewpoints. When the key criteria were found, the second survey developed for applying DEMATEL method was issued to the management of Show Chwan Memorial Hospital. Unlike the traditional multiple criteria decision-making techniques which typically assume the criteria are mutually independent; DEMATEL method does not require this assumption but further helps the decision makers in identifying the casual relationships among criteria. That is, by applying DEMATEL method, the importance of seven criteria can be determined and the causal relations among the criteria can be constructed.