Abstract
The paper deals with strengthening of the reinforced concrete beam by shape memory alloy at the place of maximum loading and deformation. A structural analysis is performed using FEM to study the behavior of the beam reinforced by steel and shape memory alloys under 3- and 4-point bending. The elasticity of the reinforced concrete beam with NiTi rods slightly increase and depends on loading type. It was revealed, that under the bending in the beam reinforced by shape memory alloy the residual deflection decreases in comparison with traditional reinforcement.
1. Introduction
Shape memory alloys (SMA), due to their pseudoelastic and good damping properties, are increasingly using in structures. SMA improve the load-bearing capacity of structures or their individual elements under static load by Almeida et al. (2020); Ayoub et al. (2004); Bykiv et al. (2020); Hamid et al. (2018). Due to high damping properties SMA are employed as the main elements in the devices to decrease the dynamic loadings of the structures by Menna et al. (2015) bridges in particular by Fang et al. (2019). Besides, SMA are considered to be the alternative strengthening of the structures or their elements being in operation in the seismic regions by Isalgue et al. (2006); Morais et al. (2017); Zafar and Andrawes (2015).
4. Conclusions
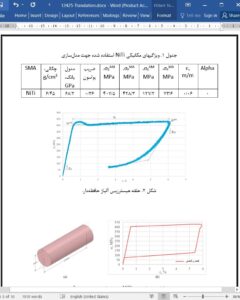
The elasticity of the reinforced concrete beam with NiTi rods slightly increase and depends of loading type. However, residual deflection reduces by 24% under 3-point bending and by 27% under 4-point bending in comparison with traditional reinforcement.
In the beam with nitinol rods, the maximum stresses are higher by 6% in the first cycle and 0.5% in the second cycle, but the residual stresses are lower by 2.3% in the first cycle and 4.3% in the second cycle, compared to the beam without nitinol rods.
Residual stresses decreased using NiTi rods by 2.3% after the first cycle; 4.3% after the second cycle. It was estimated that under 4-point bending, NiTi rods showed a better recovery effect in comparison with 3-point bending