Background
Information on prevalence of depression among children, adolescents, and adults with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is limited.
Objective To compare prevalence of depression in HS patients with that of controls.
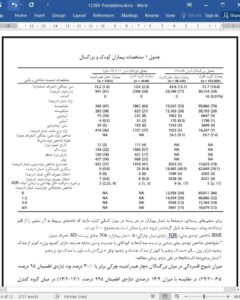
Methods Cross-sectional analysis of 38,140 adult and 1162 pediatric HS patients and controls identified using data from electronic health records. Primary outcome was prevalent depression.
Results Prevalence of depression among adults with HS was 30.0% (95% Confidence interval [CI], 29.6-30.5), compared with 16.9% (95% CI, 16.7-17.1) among controls. Among children and adolescents with HS, prevalence of depression was 11.7% (95% CI, 10.0-13.7), compared with 4.1% (95% CI, 3.6-4.7) among controls. In adjusted analyses, adults and children/adolescents with HS had 1.26 (95% CI, 1.25-1.28; P < .001) and 1.42 (95% CI, 0.999-2.01; P = .051) times the odds of having depression relative to controls, respectively.
Limitations We could not evaluate the influence of disease severity on the outcome.
Conclusion Depression is prevalent among children, adolescents, and adults with HS. Periodic screening for depression may be warranted.
CONCLUSION
Prevalence of depression among pediatric and adult patients with HS is high. Additionally, our data suggest that adult and pediatric patients with HS more commonly suffer from depression. Health care providers should be attentive to signs and symptoms of depression among children, adolescents, and adult patients with HS. Periodic screening for depression may be considered.